Difference between revisions of "Woodlands Bast Fiber Reference Collection"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (MDerrick moved page Woodland Plant Fiber Reference Collection to Woodlands Bast Fiber Reference Collection) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Note: this page is in progress. Please do not link or cite until it is finalized | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
* [[Basswood]]: Bass wood (''Tilia americana'') | * [[Basswood]]: Bass wood (''Tilia americana'') | ||
* [[Elm]]: Slippery elm (''Ulnus rubra'') | * [[Elm]]: Slippery elm (''Ulnus rubra'') | ||
| − | * [[Nettle]]: Stinging nettle (''Urtica dioca'' | + | * [[Nettle]]: Stinging nettle (''Urtica dioca'') |
* [[Dogbane]]: Dogbane (''Apocynum annabinum'') | * [[Dogbane]]: Dogbane (''Apocynum annabinum'') | ||
* [[Milkweed fiber|Milkweed]]: Common milkweed (''Aspclepias syria''), Swamp milkweed (''Aspclepias incarnate'') | * [[Milkweed fiber|Milkweed]]: Common milkweed (''Aspclepias syria''), Swamp milkweed (''Aspclepias incarnate'') | ||
| Line 83: | Line 85: | ||
| Ca, Mg, Na | | Ca, Mg, Na | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| + | * Nora Frankel, edited 4/10/18, National Museum of the American Indian | ||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
[[Category:FRIL]] | [[Category:FRIL]] | ||
[[Category: FRIL: Plant Fibers]] | [[Category: FRIL: Plant Fibers]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:25, 7 July 2023
Note: this page is in progress. Please do not link or cite until it is finalized
Description
Some images of plant fibers in the FRIL Database are from the Woodland Plant Fiber Reference Collection as the National Museum of the American Indian (NMAI). Pre-Columbian clothing, baskets, pouches, cords and mats were often made from the inner layers of bark and plants. In the northern and eastern regions of North America, the most commonly used fibers were
- Basswood: Bass wood (Tilia americana)
- Elm: Slippery elm (Ulnus rubra)
- Nettle: Stinging nettle (Urtica dioca)
- Dogbane: Dogbane (Apocynum annabinum)
- Milkweed: Common milkweed (Aspclepias syria), Swamp milkweed (Aspclepias incarnate)
A table containing a comparison of these fibers can be found here.
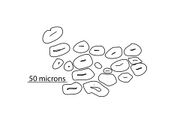
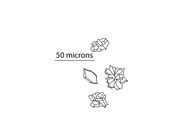
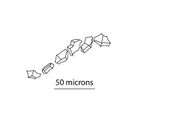
| Common name | Scientific Name | Micro-fibrillar Spin | Crystals | Crystal Diagram | Cross-section Diagram | Fiber Diameter (microns) | Fiber L:W Ratio |
EDS results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dogbane | Apocynum cannabinum | S | Calcium sulfate in parenchyma | Range: 5-35 Typical: 15-25 |
2.09 | Ca, S, Na | ||
| Nettle | Urtica dioica | S | Frequent calcium oxalate druses in parenchyma. | Range: 10-75 Typical: 15-70 |
2.7 | Ca, S | ||
| Common milkweed | Asclepias syriaca | S | Infrequent calcium oxalate druses in parenchyma, calcium sulfate in parenchyma. | Range: 10-30 Typical: 10-20 |
1.3 | Ca, S, Na | ||
| Swamp milkweed | Asclepias incarnata | S | Infrequent calcium oxalate druses in parenchyma, calcium sulfate in parenchyma. | Range: 5-25 Typical: 15-20 |
1.23 | Ca, S, Na | ||
| Basswood | Tilia americana | Z | Calcium oxalate druses and prismatic, found within fiber network. Calcium sulfate also present. |
Range: 8-20 Typical: 10-18 |
1.32 | Ca, S, Na | ||
| Slippery elm | Ulmus rubra | Z? | Frequent calcium oxalate prismatic crystals in fiber network. | Range: 4-14 Typical: 5-10 |
1.59 | Ca, Mg, Na |
Resources and Citations
- Nora Frankel, edited 4/10/18, National Museum of the American Indian