Difference between revisions of "Stearic acid"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | White, waxy fatty acid. Stearic acid occurs naturally in animal fats, [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=tallow tallow], and, to a smaller extent, vegetable fats. Lard and tallow can contain up to 30% stearic acid. Stearic acid is a long-chain saturated triglyceride with no double bonds that can be readily saponified with alkaline salts. Most commercial stearic acid products, such as U.S.P. stearic acid, contain are a mixture of 50% stearic acid, 45% [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=palmitic | + | White, waxy fatty acid. Stearic acid occurs naturally in animal fats, [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=tallow tallow], and, to a smaller extent, vegetable fats. Lard and tallow can contain up to 30% stearic acid. Stearic acid is a long-chain saturated triglyceride with no double bonds that can be readily saponified with alkaline salts. Most commercial stearic acid products, such as U.S.P. stearic acid, contain are a mixture of 50% stearic acid, 45% [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=palmitic%20acid palmitic acid], and 5% [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=oleic%20acid oleic acid]. Stearic acid is used as a lubricatant, softener, and dispersing agent in soaps, candles, lubricants, ointments, cosmetics, rubber, polishes, coatings, and food packaging. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | n-octadecanoic acid (IUPAC); Emersol 132; Promulsin; Proviscol Wax. U.S.P. stearic acid; kyselina | + | n-octadecanoic acid (IUPAC); Emersol 132; Promulsin; Proviscol Wax. U.S.P. stearic acid; kyselina stearová (Ces.); Stearinsäure (Deut.); ácido esteárico (Esp.); acide stéarique (Fr.); (It.); stearinezuur (Ned.); kwas stearynowy (Pol.); |
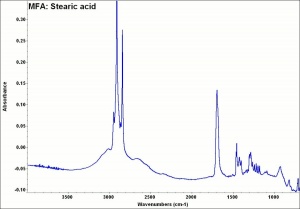
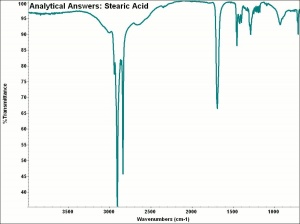
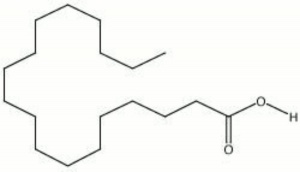
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Stearic acid.jpg~FTIR|aaiSTEARIC.jpg~FTIR|stearic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|MFA- Stearic acid.jpg~FTIR|aaiSTEARIC.jpg~FTIR|stearic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 770 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8959 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8959 | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
* ''A Glossary of Paper Conservation Terms'', Margaret Ellis (ed.), Conservation Center of the Institute of Fine Arts, New York City, 1998 | * ''A Glossary of Paper Conservation Terms'', Margaret Ellis (ed.), Conservation Center of the Institute of Fine Arts, New York City, 1998 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "stearic acid" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "stearic acid" Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [Accessed 25 Jan. 2006]. |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearic_acid (Accessed Feb. 10, 2006) | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearic_acid (Accessed Feb. 10, 2006) | ||
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Revision as of 06:25, 24 July 2013
Description
White, waxy fatty acid. Stearic acid occurs naturally in animal fats, tallow, and, to a smaller extent, vegetable fats. Lard and tallow can contain up to 30% stearic acid. Stearic acid is a long-chain saturated triglyceride with no double bonds that can be readily saponified with alkaline salts. Most commercial stearic acid products, such as U.S.P. stearic acid, contain are a mixture of 50% stearic acid, 45% palmitic acid, and 5% oleic acid. Stearic acid is used as a lubricatant, softener, and dispersing agent in soaps, candles, lubricants, ointments, cosmetics, rubber, polishes, coatings, and food packaging.
Synonyms and Related Terms
n-octadecanoic acid (IUPAC); Emersol 132; Promulsin; Proviscol Wax. U.S.P. stearic acid; kyselina stearová (Ces.); Stearinsäure (Deut.); ácido esteárico (Esp.); acide stéarique (Fr.); (It.); stearinezuur (Ned.); kwas stearynowy (Pol.);
Other Properties
Almost insoluble in water.
| Composition | CH3(CH2)16COOH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 57-11-4 |
| Melting Point | 69.6 |
| Density | 0.8390 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 284.47 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4299 |
| Boiling Point | 361-383 |
Hazards and Safety
Combustible.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Authority
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 770
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8959
- A Glossary of Paper Conservation Terms, Margaret Ellis (ed.), Conservation Center of the Institute of Fine Arts, New York City, 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "stearic acid" Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [Accessed 25 Jan. 2006].
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearic_acid (Accessed Feb. 10, 2006)
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998