Difference between revisions of "Bone ash"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A white powdery material made by calcining bones, usually from cattle. Bone ash primarily contains [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=calcium | + | A white powdery material made by calcining bones, usually from cattle. Bone ash primarily contains [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=calcium%20hydroxyapatite calcium hydroxyapatite] with small amounts of [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=magnesium%20phosphate magnesium phosphate], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=calcium%20carbonate calcium carbonate], and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=calcium%20fluoride calcium fluoride]. It is used as a polishing agent and as a flux in ceramics. Bone china can contain 25-50% bone ash. Bone ash has also been used as a pigment called [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=bone%20white bone white] in grounds for silver point drawings. |
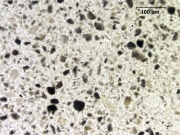
[[File:2_Calcined_bone_200X.jpg|thumb|Calcined bone]] | [[File:2_Calcined_bone_200X.jpg|thumb|Calcined bone]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * Ralph Mayer, ''A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques'', Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing) |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
| − | * | + | * Michael McCann, ''Artist Beware'', Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979 |
| − | * | + | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 |
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Revision as of 06:27, 24 July 2013
Description
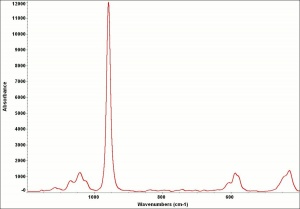
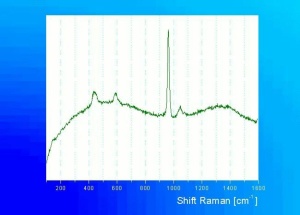
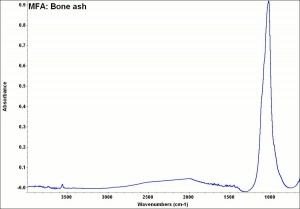
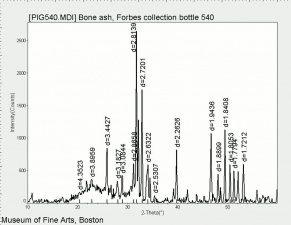
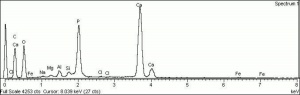
A white powdery material made by calcining bones, usually from cattle. Bone ash primarily contains calcium hydroxyapatite with small amounts of magnesium phosphate, calcium carbonate, and calcium fluoride. It is used as a polishing agent and as a flux in ceramics. Bone china can contain 25-50% bone ash. Bone ash has also been used as a pigment called bone white in grounds for silver point drawings.
Synonyms and Related Terms
bone earth; bone white (AAT); calcined bone
Hazards and Safety
Noncombustible. Inhalation of ingestion may cause slight problems.
Additional Images
Authority
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000