Difference between revisions of "Modal fiber"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A generic name for a modified [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=rayon | + | A generic name for a modified [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=rayon%20fiber rayon] fiber that has high tenacity and high wet modulus. Modal fibers were initially developed in the 1930s for industrial uses in tires, conveyor belts and hose pipes. Changes in the rayon processing, such as the spin conditions, chemical solutions, and stretching sequences, produced rayon fibers with increased crystallinity, and thus, greater strength. Additional developments in Japan in 1951 by S. Tachikawa led to the production of a modal fiber with high wet modulus called [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=polynosic%20fiber polynosic]. Modal fibers are dimensionally stable and do not shrink or get pulled out of shape when wet like many rayons. They are also wear resistant and strong while maintaining a soft, silky feel. Modal fibers have found a wide variety of uses in clothing, outerwear and household furnishings. They are often blended with [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=cotton cotton], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=wool wool], or [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=synthetic%20fiber synthetic fibers]. |
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
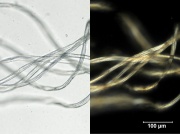
modal fibre (Br.); HWM rayon; Tenasco [Courtaulds]; Vincel [Courtaulds]; Avril [Avtex Fibers]; Moynel [Courtaulds]; modal | modal fibre (Br.); HWM rayon; Tenasco [Courtaulds]; Vincel [Courtaulds]; Avril [Avtex Fibers]; Moynel [Courtaulds]; modal | ||
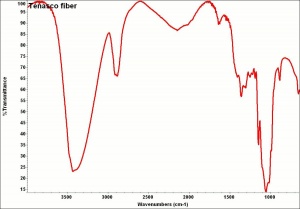
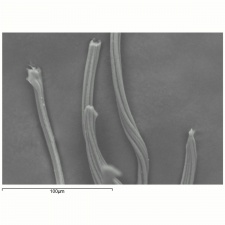
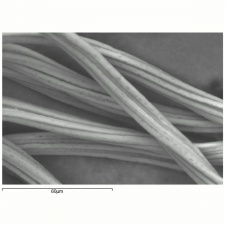
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|tenasco500m.jpg~SEM|tenasco1000m.jpg~SEM]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Tenascofiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|tenasco500m.jpg~SEM|tenasco1000m.jpg~SEM]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * J.Gordon Cook, ''Handbook of Textile Fibres:I Natural Fibres'', Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England, 1984 |
* ''Identification of Textile Materials'', The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985 | * ''Identification of Textile Materials'', The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985 | ||
Revision as of 06:35, 24 July 2013
Description
A generic name for a modified rayon fiber that has high tenacity and high wet modulus. Modal fibers were initially developed in the 1930s for industrial uses in tires, conveyor belts and hose pipes. Changes in the rayon processing, such as the spin conditions, chemical solutions, and stretching sequences, produced rayon fibers with increased crystallinity, and thus, greater strength. Additional developments in Japan in 1951 by S. Tachikawa led to the production of a modal fiber with high wet modulus called polynosic. Modal fibers are dimensionally stable and do not shrink or get pulled out of shape when wet like many rayons. They are also wear resistant and strong while maintaining a soft, silky feel. Modal fibers have found a wide variety of uses in clothing, outerwear and household furnishings. They are often blended with cotton, wool, or synthetic fibers.
Synonyms and Related Terms
modal fibre (Br.); HWM rayon; Tenasco [Courtaulds]; Vincel [Courtaulds]; Avril [Avtex Fibers]; Moynel [Courtaulds]; modal
Other Properties
Tenacity = 3 - 5 g/denier; Elongation = 6-14% (dry); 8-20 % (wet); Fiber is smooth; some have striations; Cross section is circular or bean shaped.
| Density | 1.52-1.54 |
|---|
Additional Information
G.Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:II. Man-made Fibres, 5th edition, Merrow Publishing Co., Durham, England, 1984.
Authority
- J.Gordon Cook, Handbook of Textile Fibres:I Natural Fibres, Merrow Publishing Co. , Durham, England, 1984
- Identification of Textile Materials, The Textile Institute, Manchester, England, 1985