Difference between revisions of "Brilliant Green"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | Basic Green 1; CI 42040; Pigment Green 1 (phosphotungstomolybdic acid salt); | + | Basic Green 1; CI 42040; Pigment Green 1 (phosphotungstomolybdic acid salt); Brilliantgrün (Deut.); vert brillant (Fr.); verde brillante (Esp.); verde brillante (It.); Malachite Green G; Emerald Green; Solid Green; Fast Green J; Diamond Green G; |
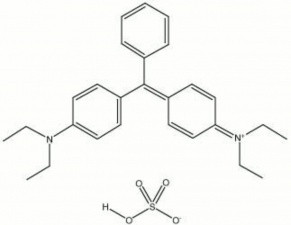
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|brilliant green.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|brilliant green.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * Monona Rossol, ''The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide'', Allworth Press, New York, 1994 |
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Brilliant Green." | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Brilliant Green." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2004. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. 20 May 2004 . |
* Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org | * Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
* Sigma Dyes, Stains and Natural Pigments, Infrared Library, Nicolet, 1991-1995 | * Sigma Dyes, Stains and Natural Pigments, Infrared Library, Nicolet, 1991-1995 | ||
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1398 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1398 | ||
Revision as of 06:42, 24 July 2013
Description
A yellowish green synthetic organic dye. Brilliant Green is an aniline based dye that was discovered in 1979 by Bindschedler and Busch. It has an absorption maximum of 623 nm and is used to dye silk, wool, leather, jute, and cotton. Brilliant green is also used in green inks, automotive paints; polymer colorants, and as an antiseptic against gram-positive microorganisms. It changes to yellow in acid at pH's below 2.6.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Basic Green 1; CI 42040; Pigment Green 1 (phosphotungstomolybdic acid salt); Brilliantgrün (Deut.); vert brillant (Fr.); verde brillante (Esp.); verde brillante (It.); Malachite Green G; Emerald Green; Solid Green; Fast Green J; Diamond Green G;
Other Properties
Soluble in water and ethanol.
| Composition | C27H34N2O4S |
|---|---|
| CAS | 633-03-4 |
| Melting Point | 210 (dec) |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 482.65 |
Hazards and Safety
Contact may cause irritation.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Authority
- Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Brilliant Green." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2004. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. 20 May 2004 .
- Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org
- Sigma Dyes, Stains and Natural Pigments, Infrared Library, Nicolet, 1991-1995
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1398