Difference between revisions of "Potassium acetate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0547.html International Chemical Safety Card] | [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/ipcsneng/neng0547.html International Chemical Safety Card] | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.609 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.609 | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 1 May 2016
Description
White, deliquescent crystals often used for humidity control. Potassium acetate is used as a dehydrating agent, textile conditioner, an ice melter, and as an additive in crystal glass. In a closed environment, a saturated solution of potassium acetate will form an equilibrium at a relative humidity of about 23% (20C).
Synonyms and Related Terms
foliated earth of tartar; acetate of potash
Other Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol. Insoluble in ether.
Deliquescent point at 20C is 23.3 % RH (see saturated salt solutions)
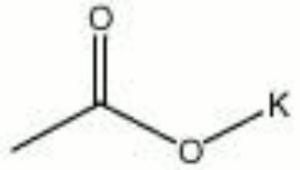
| Composition | KC2H3O2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 127-08-2 |
| Melting Point | 292 |
| Density | 1.57 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 98.14 |
Hazards and Safety
Combustible.
International Chemical Safety Card
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.609
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 7764