Difference between revisions of "Acrylic acid"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Mallinckrodt Baker: [http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/Englishhtml/a1562.htm MSDS] | Mallinckrodt Baker: [http://www.jtbaker.com/msds/Englishhtml/a1562.htm MSDS] | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 10 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 10 | ||
Revision as of 11:58, 29 April 2016
Description
A colorless, corrosive liquid that polymerizes readily in the presence of oxygen. Acrylic acid was first synthesized in 1843. It is used in the manufacture of acrylic resins.
Synonyms and Related Terms
2-propenoic acid; vinyl formic acid; acroleic acid; propene acid; ácido acrílico (Esp.); ácido 2-propenoico (Esp.)
Other Properties
Miscible with water, ethanol and ether.
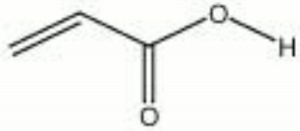
| Composition | H2C:CHCOOH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 79-10-7 |
| Melting Point | 14 |
| Density | 1.0621 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 72.06 |
| Boiling Point | 141.0 |
Hazards and Safety
Irritating to eyes, nose and skin. Toxic by inhalation. Combustible.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 10
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 132
- Irving Skeist, Handbook of Adhesives, Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, 1977 Comment: p. 528