Difference between revisions of "Diphenylcarbazone"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, ''Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology'' Archetype Publications, London, 2000, p.72. | N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, ''Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology'' Archetype Publications, London, 2000, p.72. | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* ''The Merck Index'', Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 3334 | * ''The Merck Index'', Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 3334 | ||
Revision as of 19:48, 30 April 2016
Description
Orange-red needles that are used as a colorimetric reagent for the detection of soluble Mercury salts in ethnographic and natural science collections (Odegaard et al 2000). Diphenylcarbazone dissolves in ethanol and turns blue when mercury is present.
Synonyms and Related Terms
phenyldiazenecarboxylic acid 2-phenylhydrazide; phenylazoformic acid 2-phenylhydrazide
Other Properties
Insoluble in water. Soluble in alcohol, chloroform, benzene.
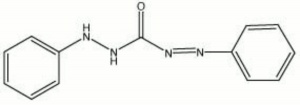
| Composition | C13H12N4O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 538-62-5 |
| Melting Point | 157 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 240.26 |
Hazards and Safety
May be harmful if ingested or inhaled. Contact may cause irritation.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Additional Information
N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology Archetype Publications, London, 2000, p.72.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 3334
- N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology, Archetype Publications, London, 2000