Difference between revisions of "Eosin"
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
M.Ballard (ed.), ''Important Early Synthetic Dyes. Chemistry, Constitution, Date, Properties.'' Conservation Analytical Laboratory, Smithsonian Institution, 1991. | M.Ballard (ed.), ''Important Early Synthetic Dyes. Chemistry, Constitution, Date, Properties.'' Conservation Analytical Laboratory, Smithsonian Institution, 1991. | ||
| − | == Authority == | + | == Authority (list of sources check for information on this record)== |
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
Revision as of 08:49, 3 November 2015
Description
A red crystalline dye composed of the Potassium, Sodium, or Lead salt of tetrabromofluorescein. First discovered by Caro in 1871, eosin is primarily used as an acid dye for producing a blood red color in Silk, Wool, Paper, Leather, and Cotton. It is also used as a histological stain, a cosmetic colorant, and a colorant in red inks. In the late 19th and early 20th century, eosin was also used as a red paint pigment. Alcoholic solutions have a strong green Autofluorescence. Eosin is not permanent and fades rapidly in sunlight.
Synonyms and Related Terms
tetrabromofluorescein; Pigment Red 90; CI 45380; D&C Red No. 22; D&C Red No. 21; Acid Red 87; Solvent Red 43; éosine (Fr.); eosina (Esp., Port.); eosin Y; eosine A; eosine G; bromeosin; bromofluoresceic acid; geranium lake; eosine yellowish
Other Properties
Soluble in ethanol. Insoluble in water (potassium and sodium salts of eosin are water soluble).
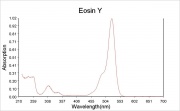
Maximum absorption wavelength = 520 nm.
Maximum emission wavelength = 540 nm.
| Composition | C20H8O5Br4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 548-26-5 |
| Melting Point | 300 |
| Molecular Weight | Mol. wt. = 647.9 |
Hazards and Safety
Causes skin irritation. Fades rapidly in sunlight.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Additional Information
M.Ballard (ed.), Important Early Synthetic Dyes. Chemistry, Constitution, Date, Properties. Conservation Analytical Laboratory, Smithsonian Institution, 1991.
Authority (list of sources check for information on this record)
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 3639
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Chemical Compound." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2004. Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. 12 May 2004 .
- Website address 1 Comment: www.probes.com/handbook/sections - gives absorption max=524 and emission max=544
- Website address 2 Comment: member.pgonline.com/~bryand/dyes/45380.htm - absorption max = 516
- Colour Index International online at www.colour-index.org Comment: discoverer and date
- Sigma Dyes, Stains and Natural Pigments, Infrared Library, Nicolet, 1991-1995 Comment: OMNIC: formula= C20H8O5Br4, CAS= 548-26-5
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998