Difference between revisions of "Butyl methacrylate"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A clear, colorless liquid used for the production of [[acrylic resin|acrylic resins]]. As early as the 1930s, solutions of polyisobutyl methacrylate (then [[Lucite®]] 45, now [[Elvacite®]] 2045) and poly n-butyl methacrylate (then Lucite® 44, now Elvacite® 2044) were used as picture varnishes (Epley 1998). By the 1960s, the resins fell into disuse because tests indicated they can crosslink. In the mid 1980s, Golden Artist colors introduced [[Golden MSA Varnish|Golden MSA varnishes]] a proprietary mixture of isobutyl and n-butyl methacrylate polymers in a mineral spirits/Stoddard solvent type mixture. Polybutyl methacrylate was also used to make [[Magna Plastic Colors|Magna Plastic]] paints from 1949 to the mid-1970s. A similar formulation is now made and sold as MSA colors. | + | A clear, colorless liquid used for the production of [[acrylic resin|acrylic resins]]. As early as the 1930s, solutions of polyisobutyl methacrylate (then [[Lucite|Lucite®]] 45, now [[Elvacite|Elvacite®]] 2045) and poly n-butyl methacrylate (then Lucite® 44, now Elvacite® 2044) were used as picture varnishes (Epley 1998). By the 1960s, the resins fell into disuse because tests indicated they can crosslink. In the mid 1980s, Golden Artist colors introduced [[Golden MSA Varnish|Golden MSA varnishes]] a proprietary mixture of isobutyl and n-butyl methacrylate polymers in a mineral spirits/Stoddard solvent type mixture. Polybutyl methacrylate was also used to make [[Magna Plastic Colors|Magna Plastic]] paints from 1949 to the mid-1970s. A similar formulation is now made and sold as MSA colors. |
See also [[polymethyl methacrylate]]. | See also [[polymethyl methacrylate]]. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
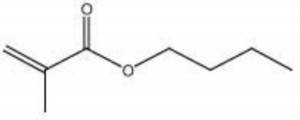
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|butyl methacrylate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|butyl methacrylate.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| + | Combustible. Flash point = 41 C Moderate fire risk. Lachrymator. Toxic by ingestion. Contact causes irritation. Potential teratogen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Crosslinks under strong fluorescent light exposure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/59652.htm MSDS] | ||
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 48: | ||
| 163-164 | | 163-164 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 65: | Line 55: | ||
[[media:download_file_357.pdf|General Characteristics of Polymers]] | [[media:download_file_357.pdf|General Characteristics of Polymers]] | ||
| + | == Resources and Citations == | ||
| − | + | * B. Epley, "The History of Synthetic Resin Varnishes", ''AIC Painting Conservation Catalog: Varnishes and Surface Coatings'', p.39, 1998. | |
| − | |||
* Paintings Specialty Group, ''Painting Conservation Catalog'', Wendy Samet (ed.), AIC, Washington, DC, 1998 | * Paintings Specialty Group, ''Painting Conservation Catalog'', Wendy Samet (ed.), AIC, Washington, DC, 1998 | ||
Revision as of 12:14, 6 August 2020
Description
A clear, colorless liquid used for the production of acrylic resins. As early as the 1930s, solutions of polyisobutyl methacrylate (then Lucite® 45, now Elvacite® 2045) and poly n-butyl methacrylate (then Lucite® 44, now Elvacite® 2044) were used as picture varnishes (Epley 1998). By the 1960s, the resins fell into disuse because tests indicated they can crosslink. In the mid 1980s, Golden Artist colors introduced Golden MSA varnishes a proprietary mixture of isobutyl and n-butyl methacrylate polymers in a mineral spirits/Stoddard solvent type mixture. Polybutyl methacrylate was also used to make Magna Plastic paints from 1949 to the mid-1970s. A similar formulation is now made and sold as MSA colors.
See also Polymethyl methacrylate.
Synonyms and Related Terms
poly (n-butylmethacrylate); pnBMA; polibutilmetacrilato (Esp.); poli (n-butilmetacrilato) (Esp.); butyl-méhacrylate (Fr.); poli butil methacrilato (It.); polibutilmetacrilato (Port.); methacrylic acid; butyl ester
Examples: Lucite® 44; Elvacite® 2044
Risks
Combustible. Flash point = 41 C Moderate fire risk. Lachrymator. Toxic by ingestion. Contact causes irritation. Potential teratogen.
Crosslinks under strong fluorescent light exposure.
Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Other Properties
Insoluble in water.
Tg = 22 C
| Composition | H3C:CCH3COOC4H9 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 97-88-1 |
| Melting Point | -75 |
| Density | 0.895 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 142.097 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4220 |
| Boiling Point | 163-164 |
Comparisons
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
General Characteristics of Polymers
Resources and Citations
- B. Epley, "The History of Synthetic Resin Varnishes", AIC Painting Conservation Catalog: Varnishes and Surface Coatings, p.39, 1998.
- Paintings Specialty Group, Painting Conservation Catalog, Wendy Samet (ed.), AIC, Washington, DC, 1998