Difference between revisions of "Red pine"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | 1) A common evergreen tree, ''Pinus resinosa'', native to northeastern North America. Red pine has a light reddish wood with a fine grain. The strong, hard wood is used for flooring, millwork, and [ | + | 1) A common evergreen tree, ''Pinus resinosa'', native to northeastern North America. Red pine has a light reddish wood with a fine grain. The strong, hard wood is used for flooring, millwork, and [[kraft%20paper|kraft pulp]]. Lumber production of red pine in the United States peaked about 1889. |
2) The primary timber tree, ''Dacrydium cupressinum'', of New Zealand. Red pine has a reddish brown wood with a straight grain. It is used for furniture, millwork, and kraft pulp. | 2) The primary timber tree, ''Dacrydium cupressinum'', of New Zealand. Red pine has a reddish brown wood with a straight grain. It is used for furniture, millwork, and kraft pulp. | ||
Revision as of 10:48, 10 May 2016
Description
1) A common evergreen tree, Pinus resinosa, native to northeastern North America. Red pine has a light reddish wood with a fine grain. The strong, hard wood is used for flooring, millwork, and kraft pulp. Lumber production of red pine in the United States peaked about 1889.
2) The primary timber tree, Dacrydium cupressinum, of New Zealand. Red pine has a reddish brown wood with a straight grain. It is used for furniture, millwork, and kraft pulp.
3): A decorative evergreen, Pinus densiflora, native to Japan. The Japanese red pine is primary used for landscaping.
Synonyms and Related Terms
1: Norway pine; Pinus resinosa
2: rima; Dacrydium cupressinum
3: Japanese red pine; Pinus densiflora
Other Properties
2: 37 ppcf
| Density | 1) 33 pcf |
|---|
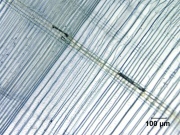
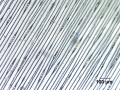
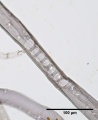
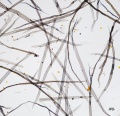
Paper fiber type: softwood, hard pine. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by the presence of large, rectangular fenestriform pits. Pits occur as singles (across the fiber) more than doubles, but both may be present. Dentate ray tracheids are present. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.4mm, width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: kraft and sulfite.
Additional Images
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 614
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- External source or communication Comment: Northern Pine Manufacturers: air-dry weight = 33 pcf
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.