Difference between revisions of "Phthalocyanine dye"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A chromophore composed of a conjugated system of double bonds that forms a color complex with a metal. Phthalocyanine type choromophores occur naturally in chlorophyll and animal blood. They were first synthesized in the 1920s and commercially introduced in the 1930s. Because they are insoluble, phthlocyanine dyes are also classified as pigments. Examples include [[phthalocyanine%20green|phthalocyanine green]] and [[phthalocyanine%20blue|phthalocyanine blue]]. The dyes are not chemically reactive and must be physically attached to the substrate with a binder or adhesive. | A chromophore composed of a conjugated system of double bonds that forms a color complex with a metal. Phthalocyanine type choromophores occur naturally in chlorophyll and animal blood. They were first synthesized in the 1920s and commercially introduced in the 1930s. Because they are insoluble, phthlocyanine dyes are also classified as pigments. Examples include [[phthalocyanine%20green|phthalocyanine green]] and [[phthalocyanine%20blue|phthalocyanine blue]]. The dyes are not chemically reactive and must be physically attached to the substrate with a binder or adhesive. | ||
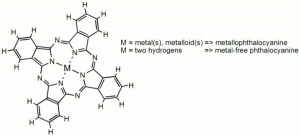
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Phthalodyekes.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
phthalocyanine dyes; phthlocyanine pigments; aza[18]annulene dye; Monastral blue | phthalocyanine dyes; phthlocyanine pigments; aza[18]annulene dye; Monastral blue | ||
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
Insoluble in water | Insoluble in water | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * Website: www.handprint.com | ||
| + | |||
* Thomas B. Brill, ''Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities'', Plenum Press, New York City, 1980 | * Thomas B. Brill, ''Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities'', Plenum Press, New York City, 1980 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phthalocyanine (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:37, 4 August 2022
Description
A chromophore composed of a conjugated system of double bonds that forms a color complex with a metal. Phthalocyanine type choromophores occur naturally in chlorophyll and animal blood. They were first synthesized in the 1920s and commercially introduced in the 1930s. Because they are insoluble, phthlocyanine dyes are also classified as pigments. Examples include Phthalocyanine green and Phthalocyanine blue. The dyes are not chemically reactive and must be physically attached to the substrate with a binder or adhesive.
Synonyms and Related Terms
phthalocyanine dyes; phthlocyanine pigments; aza[18]annulene dye; Monastral blue
Physical and Chemical Properties
Insoluble in water
Resources and Citations
- Website: www.handprint.com
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phthalocyanine (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)