Difference between revisions of "Propoxur"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "\[http:\/\/cameo\.mfa\.org\/materials\/fullrecord\.asp\?name=([^\s]+)\s(.*)\]" to "$2") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
White, odorless crystalline powder. Propoxur is a carbamate [[insecticide|insecticide]] commonly used to kill [[cockroach|cockroaches]]. It is also used in flea and tick collars. Propoxur is fast acting and has a good residual effect (5 days). | White, odorless crystalline powder. Propoxur is a carbamate [[insecticide|insecticide]] commonly used to kill [[cockroach|cockroaches]]. It is also used in flea and tick collars. Propoxur is fast acting and has a good residual effect (5 days). | ||
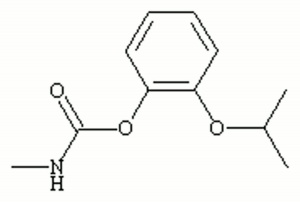
| + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|propoxurir.jpg~FTIR|propoxurstructure.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
PHC; o-isopropoxy phenyl methyl carbamate; Baygon [Mobay]; Raid®; Blattanex; Bolfo; Invisi-Gard; Isocarb; o-IMPC; Propyon; Rhoden; Sendran; Suncide; Tendex; Tugon Fliegenkugel; Unden; Undene | PHC; o-isopropoxy phenyl methyl carbamate; Baygon [Mobay]; Raid®; Blattanex; Bolfo; Invisi-Gard; Isocarb; o-IMPC; Propyon; Rhoden; Sendran; Suncide; Tendex; Tugon Fliegenkugel; Unden; Undene | ||
| − | [ | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | * Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. LD50=90-128 mg/kg | ||
| + | * Decomposes to form methyl isocyanate. | ||
| + | * May stain fabrics, plastics, paper and rubber. | ||
| + | * BASF: [https://www.americanpest.net/media/ompjpkbd/pt-250-propoxur-sds.pdf SDS] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== |
Soluble in most polar solvent. Slight soluble in water. Unstable in alkaline media. | Soluble in most polar solvent. Slight soluble in water. Unstable in alkaline media. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 91.5 | + | | 91.5 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 29: | Line 35: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * EPA: [https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-09/documents/propoxur.pdf Tech Sheet] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
Latest revision as of 13:09, 5 October 2022
Description
White, odorless crystalline powder. Propoxur is a carbamate Insecticide commonly used to kill cockroaches. It is also used in flea and tick collars. Propoxur is fast acting and has a good residual effect (5 days).
Synonyms and Related Terms
PHC; o-isopropoxy phenyl methyl carbamate; Baygon [Mobay]; Raid®; Blattanex; Bolfo; Invisi-Gard; Isocarb; o-IMPC; Propyon; Rhoden; Sendran; Suncide; Tendex; Tugon Fliegenkugel; Unden; Undene
Risks
- Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. LD50=90-128 mg/kg
- Decomposes to form methyl isocyanate.
- May stain fabrics, plastics, paper and rubber.
- BASF: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in most polar solvent. Slight soluble in water. Unstable in alkaline media.
| Composition | (CH3)2CHOC6H4OOCNHCH3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 114-26-1 |
| Melting Point | 91.5 C |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 209.2 |
Resources and Citations
- EPA: Tech Sheet
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8022
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, Biology in the Conservation of Works of Art, ICCROM, Rome, 1991
- J. Dawson, CCI Technical Bulletin, 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , Canadian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002