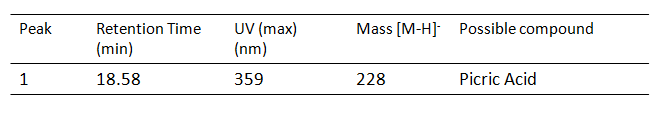Difference between revisions of "CI 10305, Picric Acid, LC"
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | == Analytical instrumentation and procedures == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Extraction''': Four different extraction solutions were tested previously in wool fibers dyed with cloth scarlet (CI 26900), prior to the HPLC-DAD-MSn analysis of historical dyed-textile samples: (a) Formic acid method - HCOOH: CH3OH (5: 95, v/v) [14]; (b) HCl method- 37%: CH3OH: H2O (2:1:1, v/v/v) [14]; (c) Oxalic acid method - C2O4H2 (0,2M): C3H6O: CH3OH: H2O (0,1: 3: 3: 4, v/v/v/v) [14]; and (d) TFA method- TFA 2M [15]. The analyses were performed in three replicates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The extraction was carried out as follows: a small sample of thread was extracted with the extraction solution in 1.5ml eppendorfs for 30 min, in 60ºC water bath, with constant agitation. After extraction, each extract was dried in a vacuum system, where the resulting dry residues were reconstituted with 50 μl H2O: MeOH (80:20,v/v). The best result was applied to all textile samples. | ||
| + | |||
'''HPLC system''': The dye analyses were performed in a Thermofinnigan Surveyor HPLC-DAD system with a Thermofinnigan Surveyor PDA 5 diode array detector (Thermofinnigan, USA), an autosampler and a pump. | '''HPLC system''': The dye analyses were performed in a Thermofinnigan Surveyor HPLC-DAD system with a Thermofinnigan Surveyor PDA 5 diode array detector (Thermofinnigan, USA), an autosampler and a pump. | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 3 October 2017
Usage History
Synonyms
C.I. 10305; 2,4,6-trinitrophenol; 1,3,5-Trinitrophenol.
Molecular Information
Molecular Formula C6H3N3O7
Molecular Weight 229.1 g/mol
Analytical instrumentation and procedures
Extraction: Four different extraction solutions were tested previously in wool fibers dyed with cloth scarlet (CI 26900), prior to the HPLC-DAD-MSn analysis of historical dyed-textile samples: (a) Formic acid method - HCOOH: CH3OH (5: 95, v/v) [14]; (b) HCl method- 37%: CH3OH: H2O (2:1:1, v/v/v) [14]; (c) Oxalic acid method - C2O4H2 (0,2M): C3H6O: CH3OH: H2O (0,1: 3: 3: 4, v/v/v/v) [14]; and (d) TFA method- TFA 2M [15]. The analyses were performed in three replicates.
The extraction was carried out as follows: a small sample of thread was extracted with the extraction solution in 1.5ml eppendorfs for 30 min, in 60ºC water bath, with constant agitation. After extraction, each extract was dried in a vacuum system, where the resulting dry residues were reconstituted with 50 μl H2O: MeOH (80:20,v/v). The best result was applied to all textile samples.
HPLC system: The dye analyses were performed in a Thermofinnigan Surveyor HPLC-DAD system with a Thermofinnigan Surveyor PDA 5 diode array detector (Thermofinnigan, USA), an autosampler and a pump.
HPLC Column: The separations were performed in Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 (Agilent, USA) with 5μm particle size column (2.1 mm x 150 mm). The column was kept at controlled temperature (35ºC). The samples were injected onto the column via a Rheodyne injector with a 25μl loop.
LC program: A solvent gradient of (A) TEA pH= 6,4 3mM and (B) pure methanolwas used at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min; 0-0,01min A:B (95:5) isocratic, 5 min A:B (90:10) isocratic, 10 min A:B (70:30) isocratic, 15 min A:B (50:50) isocratic, 30 min A:B (45:55) isocratic, 35 min A:B (30:70) isocratic, 45-55 min A:B (5:95) linear, 60-70 min A:B (95:5) linear.
LC-DAD-MSn: The analyses of dyes were performed on a LC-MS with ProStar 410 autosampler, two 212-LC chromatography pumps, a ProStar 335 diode array detector and a 500-MS ion trap mass spectrometer with an electrospray ionization (ESI) ion source (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA). Data acquisition and processing were performed using Varian MS Control 6.9 software.The separations were carried out using a Zorbax Eclipse Plus (Agilent, USA) with 5 μm particle size column (2.1 mm x 150 mm). The column was kept at controlled temperature (35ºC). The samples were injected onto the column via a Rheodyne injector with a 20 μL loop. The gradient adapted from and described in 2.3.1 was used at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min. The mass spectra were acquired in negative and positive mode depending on the structures. The optimized parameters were as follows: ion spray voltage, 4,8 kV; capillary voltage, 20 V; RF loading 80%. Nitrogen was used as nebulising and drying gas, at a pressure of 35 and 15 psi; drying gas temperature, 300ºC. The multistage MS (MSn) spectra were obtained with an isolation window of 2.0 Da, excitation energy values of 0,9 to 1,5 V and an excitation time of 10 ms.
[1]
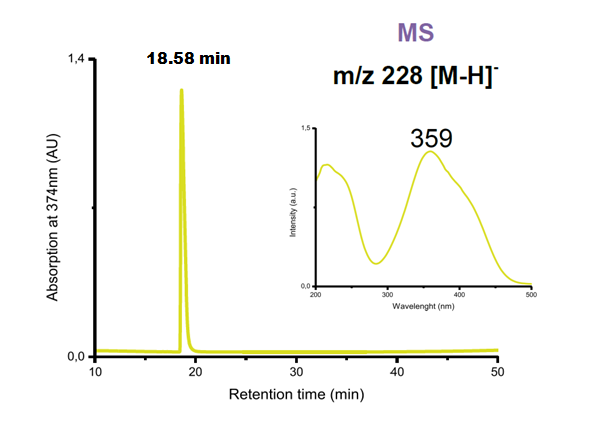
Chromatograms
Results
References
[1] Cátia Susana da Costa Nogueira Souto, "Analysis of Early Synthetic Dyes with HPLC-DAD-MS An important database for analysis of colorants used in cultural heritage", Thesis, Master Degree in Conservation and Restoration of Textiles. UNIVERSIDADE NOVA DE LISBOA, 2010.