Difference between revisions of "Turquoise"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:99.109-37-18.jpg|thumb|Roman cameo MFA 99.109]] | + | [[File:99.109-37-18.jpg|thumb|Roman cameo<br>MFA# 99.109]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | [[File:2004.2219-SC138132.jpg|thumb|Navajo bracelet<br>MFA# 2004.2219]] | |
An opaque sky-blue semiprecious gemstone. Turquoise is composed of a hydrated basic copper aluminum phosphate mineral. It was used for beads as early as 5000 BE in Mesopotamia. Major deposits were worked in Iran (Nishapur, Juh-e Zar, Kuh-i-Firouzeh) and on the Sinai Peninsula. Turquoise is also found in Siberia, Turkestan, Germany (Saxony), France, England (Cornwall), Australia and the U.S.(Mexico, Arizona, Colorado, California, New Mexico). Turquoise can be blue, greenish blue or green with inclusions of red sandstone. Turquoise is used for cabochon jewelry, inlays, beads and small carvings. | An opaque sky-blue semiprecious gemstone. Turquoise is composed of a hydrated basic copper aluminum phosphate mineral. It was used for beads as early as 5000 BE in Mesopotamia. Major deposits were worked in Iran (Nishapur, Juh-e Zar, Kuh-i-Firouzeh) and on the Sinai Peninsula. Turquoise is also found in Siberia, Turkestan, Germany (Saxony), France, England (Cornwall), Australia and the U.S.(Mexico, Arizona, Colorado, California, New Mexico). Turquoise can be blue, greenish blue or green with inclusions of red sandstone. Turquoise is used for cabochon jewelry, inlays, beads and small carvings. | ||
| − | |||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | + | [[File:Turquoisef5.jpg|thumb|Turquoise stone]] | |
turqoius; calliana; callais; Mecca stones; Türkis (Deut.); turquesa (Esp., Port.); turquoise (Fr.); turkoise (Ned.) | turqoius; calliana; callais; Mecca stones; Türkis (Deut.); turquesa (Esp., Port.); turquoise (Fr.); turkoise (Ned.) | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | + | Stone can discolor to green with wear or contact with oils and grease | |
| − | + | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | |
| − | Soluble in hot hydrochloric acid. | + | * Triclinic system, opaque, dense, cryptocrystalline to fine-grain massive. |
| + | * Fracture is conchoidal. | ||
| + | * Luster = waxy. | ||
| + | * Streak = white to pale-green. | ||
| + | * Soluble in hot hydrochloric acid. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.6-2.9 | + | | 2.6-2.9 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ! scope="row"| Refractive Index | ||
| 1.61; 1.62; 1.65 | | 1.61; 1.62; 1.65 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
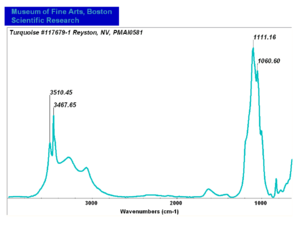
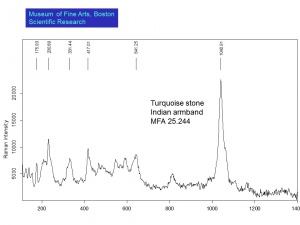
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Turquoise, Reyston NV.PNG~Raman (MFA)|Turquoise Raman.jpg~Raman (MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Turquoise, Reyston NV.PNG~Raman (MFA)|Turquoise Raman.jpg~Raman (MFA)]]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 48: | Line 40: | ||
[[media:download_file_442.pdf|Properties of Common Gemstones]] | [[media:download_file_442.pdf|Properties of Common Gemstones]] | ||
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Turquoise.shtml Turquoise] | |
| − | == | ||
* Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | * Jack Odgen, ''Jewellery of the Ancient World'', Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 49: | ||
* A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, ''Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries'', Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962 | * A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, ''Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries'', Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "turquoise" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "turquoise" [Accessed September 19, 2003]. |
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turquoise (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005) |
* ''Encyclopedia of Archaeology'', Glyn E. Daniel, ed., Thomas Y. Crowell Co., New York, 1977 | * ''Encyclopedia of Archaeology'', Glyn E. Daniel, ed., Thomas Y. Crowell Co., New York, 1977 | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 22 June 2022
Description
An opaque sky-blue semiprecious gemstone. Turquoise is composed of a hydrated basic copper aluminum phosphate mineral. It was used for beads as early as 5000 BE in Mesopotamia. Major deposits were worked in Iran (Nishapur, Juh-e Zar, Kuh-i-Firouzeh) and on the Sinai Peninsula. Turquoise is also found in Siberia, Turkestan, Germany (Saxony), France, England (Cornwall), Australia and the U.S.(Mexico, Arizona, Colorado, California, New Mexico). Turquoise can be blue, greenish blue or green with inclusions of red sandstone. Turquoise is used for cabochon jewelry, inlays, beads and small carvings.
Synonyms and Related Terms
turqoius; calliana; callais; Mecca stones; Türkis (Deut.); turquesa (Esp., Port.); turquoise (Fr.); turkoise (Ned.)
Risks
Stone can discolor to green with wear or contact with oils and grease
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Triclinic system, opaque, dense, cryptocrystalline to fine-grain massive.
- Fracture is conchoidal.
- Luster = waxy.
- Streak = white to pale-green.
- Soluble in hot hydrochloric acid.
| Composition | CuAl6(PO4)4(OH)8 - 4H2O |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 5 - 6 |
| Density | 2.6-2.9 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.61; 1.62; 1.65 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Gemstones
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Turquoise
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- R.F.Symmes, T.T.Harding, Paul Taylor, Rocks, Fossils and Gems, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1997
- A.Lucas, J.R.Harris, Ancient Egyptian Materials and Industries, Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 4th edition, 1962
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "turquoise" [Accessed September 19, 2003].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turquoise (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)
- Encyclopedia of Archaeology, Glyn E. Daniel, ed., Thomas Y. Crowell Co., New York, 1977
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 833
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979