Difference between revisions of "Brucite"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
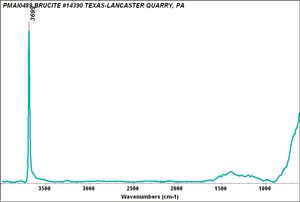
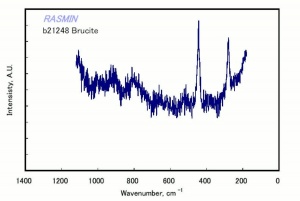
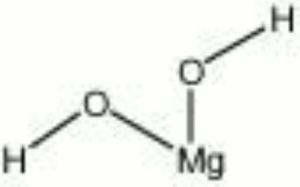
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|BRUCITE PMA.TIF~FTIR (PMA)|bruciteRS.jpg~Raman|brucite.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|BRUCITE PMA.TIF~FTIR (PMA)|bruciteRS.jpg~Raman|brucite.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * EChemi.com: [https://www.echemi.com/sds/brucite-mgoh2-pd180727138644.html SDS] | ||
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 31: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 2.39 | + | | 2.39 g/ml |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ! scope="row"| Molecular Weight | ||
| Line 34: | Line 37: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Brucite.shtml Brucite] | |
| − | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "brucite" [Accessed December 4, 2001]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "brucite" | ||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| Line 50: | Line 45: | ||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brucite (Accessed Sept. 2, 2005) |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
Revision as of 11:31, 10 May 2022
Description
A white to gray mineral composed of Magnesium hydroxide. Brucite was named for Archibald Bruce, an American mineralogist in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It occurs naturally in deposits, often with Serpentine and Dolomite, in Italy (Teulada), Sweden (Jakobsberg, Filipstad, Nordmark), Canada, and the U.S. (Nevada, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Texas). The soft mineral can be transparent to translucent with a pearly luster. Brucite is used as a refractory material as well as for a source of Magnesium metal and Magnesia.
Synonyms and Related Terms
nemalite; magnesium hydroxide; magnesium hydrate; milk of magnesia; brucita (Esp.); brucite (Port.); Brucit (Deut.); bruciet (Ned.)
Risks
- EChemi.com: SDS
Other Properties
Tabular, rhombohedron crystals, may sometimes be fibrous. Perfect cleavage parallel to prism base. Luster = waxy to vitreous. Streak = white.
| Composition | Mg(OH)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1309-42-8 |
| Mohs Hardness | 2.5 |
| Density | 2.39 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 58.32 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Brucite
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "brucite" [Accessed December 4, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brucite (Accessed Sept. 2, 2005)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- MSDS Sheet Comment: density - 2.36