Difference between revisions of "Gallic acid"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
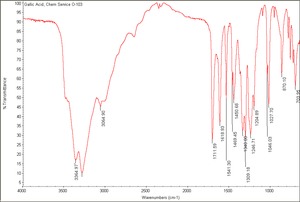
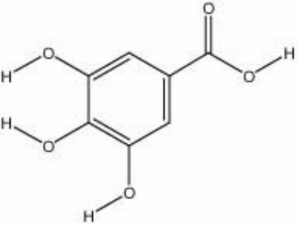
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Gallic Acid, Chem Service O-103.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|gallic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Gallic Acid, Chem Service O-103.TIF~FTIR (MFA)|gallic acid.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| + | |||
| + | Contact may cause redness or irritation. Inhalation may cause coughing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ThermoFisher: [https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC447581000&productDescription=GALLIC+ACID+MONOHYDRATE%2C+100GR&vendorId=VN00032119&countryCode=US&language=en SDS] | ||
| + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Soluble in hot water, ethanol and ether. | Soluble in hot water, ethanol and ether. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 35: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, ''Textile Analysis'', J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932 | * S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, ''Textile Analysis'', J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932 | ||
| Line 48: | Line 47: | ||
* Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | * Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, ''Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology'', U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "gallic acid" | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "gallic acid" [Accessed October 9, 2001]. |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 09:10, 19 August 2020
Description
Colorless, crystalline needles that are the primary tanning component found in galls, Divi-divi, Sumac, and Tea leaves. Gallic acid was first separated by Scheele in 1786. It is formed by the acid hydrolysis of gallotannic acid and is important in the manufacture of tannins, dyes, and writing inks. Gallic acid is also used in photography, paper manufacture, lithography, and as an analytical reagent. It was used in the 19th century to produce a dull red color on mordanted cloth.
Synonyms and Related Terms
acid of galls; 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid
Risks
Contact may cause redness or irritation. Inhalation may cause coughing.
ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in hot water, ethanol and ether.
Insoluble in benzene, chloroform.
| Composition | C6H2(OH)3COOH |
|---|---|
| CAS | 149-91-7 |
| Melting Point | 258-265 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt.=188.14 |
Resources and Citations
- S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, Textile Analysis, J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932
- F. Crace-Calvert, Dyeing and Calico Printing, Palmer & Howe, London, 1876
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "gallic acid" [Accessed October 9, 2001].