Difference between revisions of "Acetal resin"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| − | [[media: | + | [[media:download_file_284.pdf|General Characteristics of Polymers]] |
| − | [[media: | + | [[media:download_file_283.pdf|Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins]] |
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
Revision as of 11:46, 6 August 2020
Description
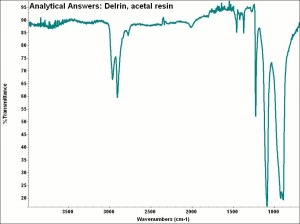
A thermoplastic polymer produced by the polymerization of formaldehyde into very long, linear oxymethylene (-O-CH2-O-CH2-) chains. Polyacetal was first produced in 1959 by DuPont under the name Delrin®. The highly crystalline resin is glossy, dense, stiff and strong. Among the toughest and most fatigue resistance of commercial thermoplastics, it is often used as a metal replacement. Acetal resin is resistant to moisture, heat, chemicals and solvents, but is sensitive to temperature. It can be metal plated, injection molded, welded, machined or extruded. Acetal resin is used for mechanical parts (gears, bushings), pipes, automotive parts, communication equipment, videocassettes, and cosmetic containers.
Synonyms and Related Terms
AC; polyacetal; resina acetálica (Esp.); poliacetal (Esp.); acétal (Fr.); resina de acetal (Port.); polyoxymethylene; POM: polyoxide; polyether; polyformaldehyde
Examples: Delrin® [DuPont]; Celcon® [Ticona]; Hostaform® [Ticona]; Ultraform® [BASF];
Risks
Combustible but very slow burning. Decomposes at high temperatures. May produce formaldehyde on decomposition.
Other Properties
Soluble in dimethylformamide, benzyl alcohol. Insoluble in methanol, diethyl ether, aliphatic hydrocarbons. Burns soot-free. Resistant to acids, and alkalis.
TAP Plastics: Technical data sheet
| Melting Point | 165-175 |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.425 |
Comparisons
General Characteristics of Polymers
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 791
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- ASTM, Standard Terminology Relating to Thermophysical Properties, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 6, Paints, Related Coatings and Aromatics, ASTM, E1142, 695-696, Jul-94
- M.Kaufman, The First Century of Plastics, The Plastics and Rubber Institute, London, 1963
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- History of Plastics: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html