Difference between revisions of "Balsam fir"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[File:30_Balsam Fir_100x_Rad.jpg|thumb|Balsam fir (''Abies balsamea'')]] | [[File:30_Balsam Fir_100x_Rad.jpg|thumb|Balsam fir (''Abies balsamea'')]] | ||
| − | + | [[File:30_Balsam Fir_100x_Tan.jpg|thumb|Balsam fir (''Abies balsamea'')]] | |
==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
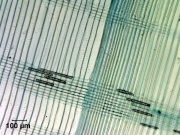
Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by large taxodiod ray parenchyma pits. Pits are frequently 2-3 across in horizontal rows. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.5mm; width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: [[sulfite process|sulfite]] or [[kraft process|kraft]]. | Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by large taxodiod ray parenchyma pits. Pits are frequently 2-3 across in horizontal rows. Appearance with [[Graff "C" stain]]: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.5mm; width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: [[sulfite process|sulfite]] or [[kraft process|kraft]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional Images == | == Additional Images == | ||
Revision as of 14:32, 3 September 2020
Description
An evergreen coniferous tree, Abies balsamea, native to the northeastern United States and Canada. The fragrant, light yellowish brown balsam fir timber has a coarse but even grain. The wood is brittle and not very durable. It is used for packing boxes and paper pulp. Balsam fir produce a viscous oleoresin called Canada balsam.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Abies balsamea; bálsamo de abeto (Esp.); fir balsam; pine fir; balm of Gilead fir "
Physical and Chemical Properties
Paper fiber type: Softwood. Using transmitted light microscopy, fibers are identified by large taxodiod ray parenchyma pits. Pits are frequently 2-3 across in horizontal rows. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: varies with pulping and bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 3.5mm; width 30-40μm. Common pulping method: sulfite or kraft.
Additional Images
- 30 Balsam Fir 100x Tan.jpg
Balsam fir (Abies balsamea)
- 30 Balsam Fir 100x Tran.jpg
Balsam fir (Abies balsamea)
Resources and Citations
- Alden Identification Services, Microscopic Wood Identification: Link
- H. A. Alden, A.C. Wiedenhoeft, "Qualified Determination of Provenance of Wood of the Firs (Abies spp. Mill) Using Microscopic Features of Rays: An Aid to Conservators, Curators and Art Historians" AIC Poster, reprinted online at http://www.si.edu/scmre/abies.html
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 83
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Kurt Wehlte, The Materials and Techniques of Painting, Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1975
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.