Difference between revisions of "Bendiocarb"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==Resources and Citations | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
* Bendiocarb regulation information: [http://ipcm.wisc.edu/news/misc/Bendiocarb.htm Website] | * Bendiocarb regulation information: [http://ipcm.wisc.edu/news/misc/Bendiocarb.htm Website] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:46, 2 May 2022
Description
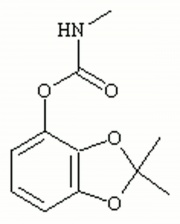
A toxic, white, nonvolatile powder that is as a carbamate type Insecticide. Bendiocarb works on contact and by ingestion and it is often used for cockroaches. Product information for Ficam® W, indicates that it does not damage paints, plastics, or fabrics, and that it is noncorrosive. Bendiocarb is stable and can provide residual control for months.
Synonyms and Related Terms
2,2-dimethyl-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl methylcarbamate; Ficam W[Fisons]; Turcam; Niomil; Seedox; Tattoo; Multamat; Garvox; Dycarb
Risks
- Toxic by ingestion and skin absorption.
- NIH: Information
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Slightly soluble in water and hexane.
- Stable to heat and light.
| Composition | C11H13NO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 22781-23-3 |
| Melting Point | 129-130 C |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 223.23 |
Resources and Citations
- Bendiocarb regulation information: Website
- Nancy Odegaard, Alyce Sadongei, and associates, Old Poisons, New Problems, Altimira, Walnut Creek, CA, 2005
- Lynda A. Zycherman, J.Richard Schrock, A Guide to Museum Pest Control, FAIC and Association of Systematics Collections, Washington DC, 1988
- J. Dawson, CCI Technical Bulletin, 'Solving Museum Insect Problems: Chemical Control' , Canadian Conservation Institute, Ottawa, No. 15
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1063
- Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002