Difference between revisions of "Cobalt blue"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:1997.182-SC8165.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:1997.182-SC8165.jpg|thumb|Chinese style bottle<br>MFA# 1997.182]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | [[File:08.475-CR10038-d1.jpg|thumb|]] | + | [[File:08.475-CR10038-d1.jpg|thumb|Dutch candlestick<br>MFA# 08.475]] |
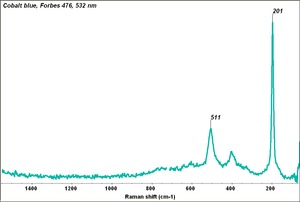
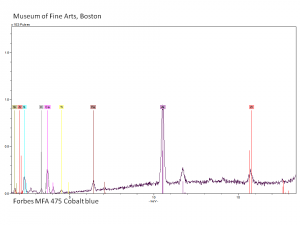
A clear blue pigment. (Some early varieties possessed a greenish tinge.) Cobalt blue is composed of a double oxide of cobalt and aluminum, also called cobaltous aluminate. It is resistant to weathering, sunlight, acids, and alkalis. Though possibly discovered earlier, the process for making cobalt blue by heating [[Cobaltous phosphate|cobalt phosphate]] with [[alumina]] was first published by L.J.Thénard in France in 1803/4 based on experiments he had carried out in 1802. Leithner discovered an alternate process for making cobalt blue from [[cobaltous arsenate|cobalt arsenate]] and alumina. By the early 19th century, cobalt blue was sold as an artists pigment as a replacement for smalt and ultramarine, although it has always been relatively costly. The pigment has been identified in French and British paintings as early as 1806/07. In recent years, the cobalt blue hue has been imitated using mixtures of [[ultramarine blue, synthetic|ultramarine]] and [[phthalocyanine blue|phthalocyanine]]. The saturated cobalt blue color in glazes and glassware is produced by [[cobaltic oxide|cobalt oxide]]. | A clear blue pigment. (Some early varieties possessed a greenish tinge.) Cobalt blue is composed of a double oxide of cobalt and aluminum, also called cobaltous aluminate. It is resistant to weathering, sunlight, acids, and alkalis. Though possibly discovered earlier, the process for making cobalt blue by heating [[Cobaltous phosphate|cobalt phosphate]] with [[alumina]] was first published by L.J.Thénard in France in 1803/4 based on experiments he had carried out in 1802. Leithner discovered an alternate process for making cobalt blue from [[cobaltous arsenate|cobalt arsenate]] and alumina. By the early 19th century, cobalt blue was sold as an artists pigment as a replacement for smalt and ultramarine, although it has always been relatively costly. The pigment has been identified in French and British paintings as early as 1806/07. In recent years, the cobalt blue hue has been imitated using mixtures of [[ultramarine blue, synthetic|ultramarine]] and [[phthalocyanine blue|phthalocyanine]]. The saturated cobalt blue color in glazes and glassware is produced by [[cobaltic oxide|cobalt oxide]]. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
cobalt aluminate; Pigment Blue 28; CI 77346; Thénard's blue; Kobaltblau (Deut.); bleu de Thénard (Fr.); bleu de cobalt (Fr.); cobaltblauw (Ned.); blu di cobalto (It.); blu di Therard (It.); mple toy kobaltioy (Gr.); azul de cobalto (Esp.); azul cobalto (Port.); cobalt ultramarine; cobaltous aluminate; king's blue; Olympia blue; Vienna blue; Vienna ultramarine; Leyden blue; Hungary blue; Dresden blue; azure cobalt; Gahn's blue; Leithner blue; new blue; | cobalt aluminate; Pigment Blue 28; CI 77346; Thénard's blue; Kobaltblau (Deut.); bleu de Thénard (Fr.); bleu de cobalt (Fr.); cobaltblauw (Ned.); blu di cobalto (It.); blu di Therard (It.); mple toy kobaltioy (Gr.); azul de cobalto (Esp.); azul cobalto (Port.); cobalt ultramarine; cobaltous aluminate; king's blue; Olympia blue; Vienna blue; Vienna ultramarine; Leyden blue; Hungary blue; Dresden blue; azure cobalt; Gahn's blue; Leithner blue; new blue; | ||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| + | * Skin contact may cause allergies, especially on elbows, neck and ankles. | ||
| + | * Chronic inhalation may cause asthma. | ||
| + | * Ingestion may cause vomiting, diarrhea and the sensation of hotness. | ||
| + | * Gamblin Colors: [https://gamblincolors.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/SDSDryPigmentCobaltBlue.pdf SDS] | ||
==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ==Physical and Chemical Properties== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 35: | ||
| 1.66-1.74 | | 1.66-1.74 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Comparisons == | == Comparisons == | ||
| Line 86: | Line 83: | ||
* Website address 1 Comment: Pigments Through the Ages: http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/coblue.html | * Website address 1 Comment: Pigments Through the Ages: http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/coblue.html | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobalt_blue (Accessed Jan. 15, 2006) |
* ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.74 (blue), >1.78 (red) | * ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'', Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.74 (blue), >1.78 (red) | ||
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 30 May 2022
Description
A clear blue pigment. (Some early varieties possessed a greenish tinge.) Cobalt blue is composed of a double oxide of cobalt and aluminum, also called cobaltous aluminate. It is resistant to weathering, sunlight, acids, and alkalis. Though possibly discovered earlier, the process for making cobalt blue by heating cobalt phosphate with Alumina was first published by L.J.Thénard in France in 1803/4 based on experiments he had carried out in 1802. Leithner discovered an alternate process for making cobalt blue from cobalt arsenate and alumina. By the early 19th century, cobalt blue was sold as an artists pigment as a replacement for smalt and ultramarine, although it has always been relatively costly. The pigment has been identified in French and British paintings as early as 1806/07. In recent years, the cobalt blue hue has been imitated using mixtures of ultramarine and phthalocyanine. The saturated cobalt blue color in glazes and glassware is produced by cobalt oxide.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cobalt aluminate; Pigment Blue 28; CI 77346; Thénard's blue; Kobaltblau (Deut.); bleu de Thénard (Fr.); bleu de cobalt (Fr.); cobaltblauw (Ned.); blu di cobalto (It.); blu di Therard (It.); mple toy kobaltioy (Gr.); azul de cobalto (Esp.); azul cobalto (Port.); cobalt ultramarine; cobaltous aluminate; king's blue; Olympia blue; Vienna blue; Vienna ultramarine; Leyden blue; Hungary blue; Dresden blue; azure cobalt; Gahn's blue; Leithner blue; new blue;
Risks
- Skin contact may cause allergies, especially on elbows, neck and ankles.
- Chronic inhalation may cause asthma.
- Ingestion may cause vomiting, diarrhea and the sensation of hotness.
- Gamblin Colors: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
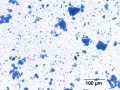
- Irregular to rounded blue particles with a ‘crusty’ surface, no birefringence, no pleochroism.
- Appears red through Chelsea filter.
- Unaffected by acids, alkalis, light, and heat.
- Strong Siccative properties in oil on account of the cobalt content.
| Composition | CoO.Al2O3 |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.83 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.66-1.74 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common Blue Pigments
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- A. Roy, “Cobalt Blue”, Artists’ Pigments: A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics, Volume 4, B. Berrie (ed.), Archetype Publications, London 2007.
- Pigments Through the Ages: Cobalt blue Record content reviewed by EU-Artech November 2007.
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: p. 108
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Ashok Roy, Contributed information, November 2007.
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: "Pigments"
- M. Doerner, The Materials of the Artist, Harcourt, Brace & Co., 1934
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980
- David Bomford, Jo Kirby, John Leighton, Ashok Roy, Art in the Making:Impressionism, National Gallery, London, 1990
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 611
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Website address 1 Comment: Pigments Through the Ages: http://webexhibits.org/pigments/indiv/overview/coblue.html
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cobalt_blue (Accessed Jan. 15, 2006)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.74 (blue), >1.78 (red)
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000