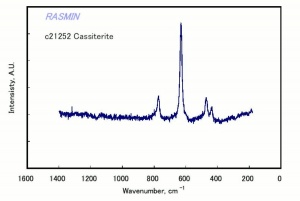
Difference between revisions of "Cassiterite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A hard, dense, brown to black mineral composed of [[ | + | A hard, dense, brown to black mineral composed of [[stannic oxide|Tin dioxide]]. Cassiterite is the principal ore of [[tin]]. Starting in the 15th century, cassiterite was mined in Saxony and Bohemia. Currently it is mined in southeast Asia (Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia), Bolivia (Llallagua), Nigeria, Russia, England (Cornwall), and the U.S. (Virginia, Washington, California). Cassiterite has a dull metallic luster and can be transparent to opaque. It has occasionally been used as a gemstone. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* Streak = white, gray or brown. | * Streak = white, gray or brown. | ||
* Insoluble in acids. | * Insoluble in acids. | ||
| − | * Pleochroism. High | + | * Pleochroism. High birefringence under crossed polars. Straight extinction. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
* Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Cassiterite.shtml Cassiterite] | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Cassiterite.shtml Cassiterite] | ||
| − | |||
* Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | * Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, ''Pigment Compendium'', Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004 | ||
| − | |||
* Henry Hodges, ''Artifacts: An Introduction to Early Materials and Technology'', Ronald P. Frye, Kingston, Canada, 1988 | * Henry Hodges, ''Artifacts: An Introduction to Early Materials and Technology'', Ronald P. Frye, Kingston, Canada, 1988 | ||
| − | |||
* Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | * Robert Fournier, ''Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery'', Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cassiterite" [Accessed December 11, 2001]. | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cassiterite" [Accessed December 11, 2001]. | ||
| − | |||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | |||
* Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cassiterite (accessed Sept 2 2005) | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cassiterite (accessed Sept 2 2005) | ||
| − | |||
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
| − | |||
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | |||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | |||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Revision as of 10:18, 15 May 2023
Description
A hard, dense, brown to black mineral composed of Tin dioxide. Cassiterite is the principal ore of Tin. Starting in the 15th century, cassiterite was mined in Saxony and Bohemia. Currently it is mined in southeast Asia (Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia), Bolivia (Llallagua), Nigeria, Russia, England (Cornwall), and the U.S. (Virginia, Washington, California). Cassiterite has a dull metallic luster and can be transparent to opaque. It has occasionally been used as a gemstone.
Synonyms and Related Terms
tinstone; tin stone; wood tin; stream tin; Zinnstein (Deut.); Kassiterit (Deut.); cassitérite (Fr.); casiterita (Esp.); cassiterite (Port.); cassiteriet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Tetragonal crystal system with prisms, pyramids or fibers.
- Good cleavage in two directions.
- Fracture = uneven.
- Luster = adamantine to dull.
- Streak = white, gray or brown.
- Insoluble in acids.
- Pleochroism. High birefringence under crossed polars. Straight extinction.
| Composition | SnO2 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 6.0 - 7.0 |
| Density | 6.8-7.1 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | about 2.0 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Cassiterite
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- Henry Hodges, Artifacts: An Introduction to Early Materials and Technology, Ronald P. Frye, Kingston, Canada, 1988
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "cassiterite" [Accessed December 11, 2001].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cassiterite (accessed Sept 2 2005)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998