Difference between revisions of "Lampblack"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A type of carbon black obtained from the soot of burned [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=fat fat], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=oil oil], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=tar tar], or [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=natural | + | A type of carbon black obtained from the soot of burned [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=fat fat], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=oil oil], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=tar tar], or [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=natural%20resin resin]. Lampblack is soft bluish-black pigment that is very stable and unaffected by [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=visible%20radiation light], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=acid acids], and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=alkali alkalis]. It was often mixed with [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=lead%20white lead white] to produce a gray pigment. Lampblack may contain a small percentage of residual fats, oils, or resins. This makes it mix poorly with [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=water water] and also makes [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=linseed%20oil linseed oil] dry slowly into a soft film. [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Umber Umber] was often added to the mixture as a drier. For use as a [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=watercolor%20paint watercolor], lampblack was mixed with [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=glue glue], prepared in sticks and sold as [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=India%20ink India ink]. Lampblack was one of the major black pigment in early American house paints (Newman and Farrell 1994). Currently lampblack is used as a black pigment in [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=cement cements], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=ceramic ceramics], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=ink inks], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=linoleum linoleum], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=crayon crayons], shoe polishes, and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=carbon%20paper carbon paper]. |
| − | See also [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=bone | + | See also [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=bone%20black bone black], [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=charcoal%20black charcoal black], and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=vine%20black vine black]. |
[[File:lampblack C100x.jpg|thumb|lampblack]] | [[File:lampblack C100x.jpg|thumb|lampblack]] | ||
Revision as of 11:03, 13 June 2013
Description
A type of carbon black obtained from the soot of burned fat, oil, tar, or resin. Lampblack is soft bluish-black pigment that is very stable and unaffected by light, acids, and alkalis. It was often mixed with lead white to produce a gray pigment. Lampblack may contain a small percentage of residual fats, oils, or resins. This makes it mix poorly with water and also makes linseed oil dry slowly into a soft film. Umber was often added to the mixture as a drier. For use as a watercolor, lampblack was mixed with glue, prepared in sticks and sold as India ink. Lampblack was one of the major black pigment in early American house paints (Newman and Farrell 1994). Currently lampblack is used as a black pigment in cements, ceramics, inks, linoleum, crayons, shoe polishes, and carbon paper.
See also bone black, charcoal black, and vine black.
Synonyms and Related Terms
lamp black; carbon black; Pigment Black 6; CI 77266; Lampenschwarz (Deut.); Flamruss (Deut.); negro de humo (Esp.); lamppumusta (Fin.); noir de fume (Fr.); noir de bougie (Fr.); karboyno (Gr.); nero di lampada (It.); bistro (It.); ner d'olio (It.); nero fiamma (It.); nero di fumo (It.); lampenzwart (Ned.); negro de fumo (Port.); lamp-black; smoke black; soot black; oil black; flame black; blacking; blue black; Germantown black
Other Properties
ASTM (1999) lightfastness = I (excellent)
| Composition | carbon |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.77 |
| Refractive Index | opaque |
Hazards and Safety
Repeated skin contact may lead to skin cancer due to impurities. Chronic inhalation may cause irritation to sinus and lung tissue. Nonflammable.
Additional Information
J.Winter, "The Characterization of Pigments Based on Carbon" Studies in Conservation, 28:49-66, 1983. R. Newman, E. Farrell, "House Paint Pigments" in Paint in America, R. Moss ed., Preservation Press, NY 1994
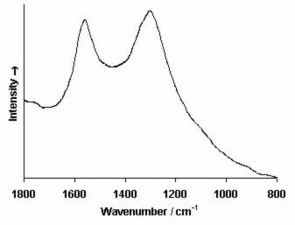
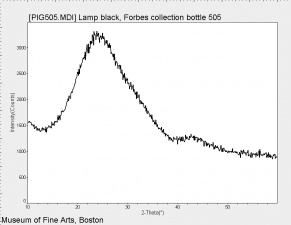
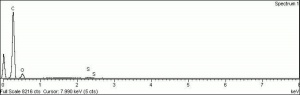
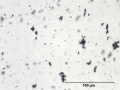
Additional Images
Authority
- Thomas Gregory, Thomas Gregory, The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Reinhold Publishing, New York, 3rd ed., 1942 Comment: Syn= Germantown black
- Richard S. Lewis, Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry #1056
- The Dictionary of Art, Grove's Dictionaries Inc., New York, 1996 Comment: 'Pigment'
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Reed Kay, Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Michael McCann, Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- R.D. Harley, R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- R. Newman, E. Farrell, R. Newman, E. Farrell, 'House Paint Pigments', Paint in America , R. Moss ed., Preservation Press, New York City, 1994
- Monona Rossol, Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- Website address 1, Website address 1 Comment: http://www.coloria.net/varita.htm - foreign language equivalent terms
- Random House, Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000