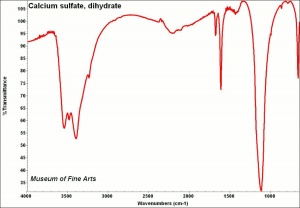
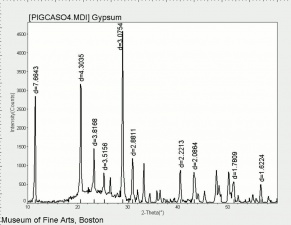
Difference between revisions of "Calcium sulfate, dihydrate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1753 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1753 | ||
Revision as of 06:22, 24 July 2013
Description
White lumps or powder that is commonly called by its mineral name of gypsum. Calcium sulfate dihydrate is used in the manufacture of portland cement. Gypsum is also used as a filler and pigment in paints, enamels, glazes and paper.
Synonyms and Related Terms
native calcium sulfate; precipitated calcium sulfate; gypsum; alabaster; selenite; terra alba; satinite; mineral white; satin spar; light spar; Pigment White 25
Other Properties
Soluble in water. Slightly soluble in glycerol. Insoluble in most organic solvents. Gypsum fluoresces purple.
| Composition | CaSO4-2H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 13397-24-5 |
| Mohs Hardness | 1.5 - 2.0 |
| Melting Point | 100-150 |
| Density | 2.32-2.36 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 172.2 |
| Refractive Index | 1.520; 1.530; 1.523 |
Hazards and Safety
Noncombustible.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Authority
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 1753