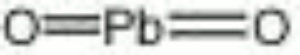Difference between revisions of "Lead dioxide"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| − | lead (IV) oxide; brown lead oxide; anhydrous plumbic acid; lead peroxide; lead superoxide; magistry of lead; precipitated oxide of lead; plattnerite; oxid | + | lead (IV) oxide; brown lead oxide; anhydrous plumbic acid; lead peroxide; lead superoxide; magistry of lead; precipitated oxide of lead; plattnerite; oxid olovièitý (Ces.); plumbic acid (when hydrated) |
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|lead dioxide.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|lead dioxide.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
| − | * | + | * Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, ''Technology and Conservation'', Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985 |
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5424 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5424 | ||
Revision as of 06:23, 24 July 2013
Description
A dark brown powder that occurs in nature as the mineral plattnerite. Lead dioxide is used to make the striking surface of matches, the electrodes in lead acid batteries, and as a mordant. It is also used as an oxidizing agent in the manufacture of dyes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
lead (IV) oxide; brown lead oxide; anhydrous plumbic acid; lead peroxide; lead superoxide; magistry of lead; precipitated oxide of lead; plattnerite; oxid olovièitý (Ces.); plumbic acid (when hydrated)
Other Properties
Soluble in hydrochloric acid with the evolution of chlorine. Soluble in dilute nitric acid in the presence of peroxide or oxalic acid. Soluble in hot alkaline solutions and glacial acetic acid.
| Composition | PbO2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1309-60-0 |
| Melting Point | 290 (dec) |
| Density | 9.38 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 239.2 |
Hazards and Safety
Fire risk in contact with organic materials.
Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Skin contact may cause irritation or ulcers. Carcinogen, teratogen, suspected mutagen.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Authority
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 5424
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_dioxide (Accessed Feb. 2, 2006)