Difference between revisions of "Diphenylcarbazide"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 3333 | * ''The Merck Index'', Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 3333 | ||
| − | * | + | * N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, ''Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology'', Archetype Publications, London, 2000 |
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Revision as of 06:28, 24 July 2013
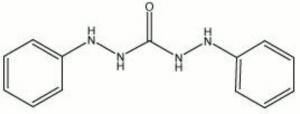
Description
White crystalline powder used for the colorimetric detection of chromium in metals, tanned leather, and pigments (Odegaard et al 2000). Diphenylcarbazide gives a dark blue-violet positive reaction. Other metals, such as cadmium, mercury, magnesium, silver, nickel, tin, and aluminum will also react with diphenylcarbazide.
Synonyms and Related Terms
2,2'-diphenylcarbonic dihydrazide; 1,5-diphenylcarbazide; S-diphenylcarbazide; DPC
Other Properties
Slightly soluble in water. Soluble in hot alcohol, acetone, glacial acetic acid
| Composition | C33H14N4O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 140-22-7 |
| Melting Point | 168-171 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 242.27 |
Hazards and Safety
Degrades in light.
May be harmful by ingestion or inhalation. Contact may cause irritation.
Mallinckrodt Baker: MSDS
Additional Information
N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology Archetype Publications, London, 2000, p.44.
Authority
- The Merck Index, Susan Budavari (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Whitehouse Station, NJ, 12th Edition, 1996 Comment: entry 3333
- N.Odegaard, S.Carroll, W.Zimmt, Material Characterization Tests for Objects of Art and Archaeology, Archetype Publications, London, 2000