Difference between revisions of "Kapok"
(username removed) |
(username removed) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | Short, lightweight [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=cellulose cellulosic] fibers obtained from the seeds of the silk cotton tree, ''Ceiba pentandra'', primarily grown in Java, Africa, Brazil, India, and Central America. Kapok is composed of 43% [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=alpha | + | Short, lightweight [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=cellulose cellulosic] fibers obtained from the seeds of the silk cotton tree, ''Ceiba pentandra'', primarily grown in Java, Africa, Brazil, India, and Central America. Kapok is composed of 43% [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=alpha%20cellulose alpha cellulose], 24% pentose, 15% [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=lignin lignin], and 6.6% uronic anhydride. The soft fibers have a smooth surface and are transparent. Kapok is buoyant and will support up to 30 times its own weight. The fluffy fibers are too brittle to spin and are used for filling mattresses, upholstery, and life jackets. |
| − | See also [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=bombax bombax] and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Indian | + | See also [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=bombax bombax] and [http://cameo.mfa.org/materials/fullrecord.asp?name=Indian%20kapok Indian kapok]. |
[[File:Kapok_tree_det.jpg|thumb|Silk cotton tree | [[File:Kapok_tree_det.jpg|thumb|Silk cotton tree | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
silk cotton tree (''Ceiba pentandra''); ceiba; samauma; Illiani silk; Java cotton; vegetable down; Java kapok; simal; balsam fiber; pochote; red silk cotton; Kapokbaum (Deut.); kapok (Fr.,Esp., Ned.) | silk cotton tree (''Ceiba pentandra''); ceiba; samauma; Illiani silk; Java cotton; vegetable down; Java kapok; simal; balsam fiber; pochote; red silk cotton; Kapokbaum (Deut.); kapok (Fr.,Esp., Ned.) | ||
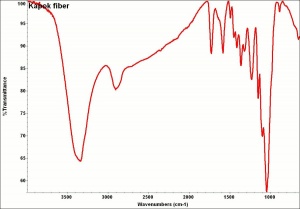
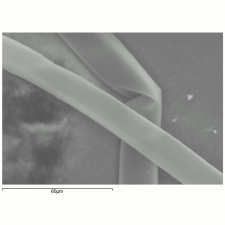
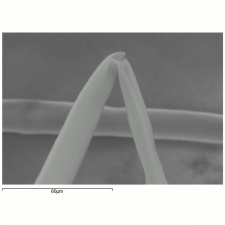
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|kapok1000am.jpg~SEM|kapok1000bm.jpg~SEM]]] | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Kapokfiberkj1.jpg~FTIR|kapok1000am.jpg~SEM|kapok1000bm.jpg~SEM]]] |
== Other Properties == | == Other Properties == | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
File:Kapok.bark_HI.BG.jpg|Kapok tree ''Ceiba pentandra'' | File:Kapok.bark_HI.BG.jpg|Kapok tree ''Ceiba pentandra'' | ||
File:Kapok 200X BF.POL.jpg|Kapok fibers | File:Kapok 200X BF.POL.jpg|Kapok fibers | ||
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
== Authority == | == Authority == | ||
| − | * | + | * Hoechst Celanese Corporation, ''Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology'' (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990 |
| − | * | + | * S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, ''Textile Analysis'', J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932 |
| − | * | + | * Rosalie Rosso King, ''Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation'', Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985 |
| − | * | + | * F. H. Titmuss, ''Commercial Timbers of the World'', The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965 |
| − | * | + | * Marjory L. Joseph, ''Introductory Textile Science'', Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986 |
| − | * | + | * Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, ''Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them'', American Book Company, New York City, 1937 |
* Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kapok (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005) | * Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kapok (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005) | ||
| − | * | + | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 430 |
| − | * | + | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
| − | * | + | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 |
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
Revision as of 06:37, 24 July 2013
Description
Short, lightweight cellulosic fibers obtained from the seeds of the silk cotton tree, Ceiba pentandra, primarily grown in Java, Africa, Brazil, India, and Central America. Kapok is composed of 43% alpha cellulose, 24% pentose, 15% lignin, and 6.6% uronic anhydride. The soft fibers have a smooth surface and are transparent. Kapok is buoyant and will support up to 30 times its own weight. The fluffy fibers are too brittle to spin and are used for filling mattresses, upholstery, and life jackets.
See also bombax and Indian kapok.
Synonyms and Related Terms
silk cotton tree (Ceiba pentandra); ceiba; samauma; Illiani silk; Java cotton; vegetable down; Java kapok; simal; balsam fiber; pochote; red silk cotton; Kapokbaum (Deut.); kapok (Fr.,Esp., Ned.)
Other Properties
Fiber length = 20 - 32 mm (0.75-1.25 inches); Diameter = 20 micrometers; Cross section is oval or circular.
Hazards and Safety
Combustible.
Comparisons
Additional Images
Authority
- Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Dictionary of Fiber & Textile Technology (older version called Man-made Fiber and Textile Dictionary, 1965), Hoechst Celanese Corporation, Charlotte NC, 1990
- S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, Textile Analysis, J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932
- Rosalie Rosso King, Textile Identification, Conservation, and Preservation, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985
- F. H. Titmuss, Commercial Timbers of the World, The Technical Press Ltd., London, 1965
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- Edward Reich, Carlton J. Siegler, Consumer Goods: How to Know and Use Them, American Book Company, New York City, 1937
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kapok (Accessed Sept. 7, 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 430
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000