Difference between revisions of "Acanthite"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | A gray to black metallic mineral of [[ | + | A gray to black metallic mineral of [[silver%20sulfide|silver sulfide]]. Acanthite occurs in hydrothermal deposits and as a corrosion product of [[silver|silver]]. Large crystals of acanthite have been mined in Norway (Kongsberg), Mexico (Pachuca, Guanajuato, Zacatecas) and the U.S. (Nevada, Colorado, Montana). On silver, acanthite crystals can appear as black, shiny, acanthus-like leaflets. At temperatures above 173 C, acanthite is converted to [[argentite|argentite]]. |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
Revision as of 13:35, 6 January 2014
Description
A gray to black metallic mineral of Silver sulfide. Acanthite occurs in hydrothermal deposits and as a corrosion product of Silver. Large crystals of acanthite have been mined in Norway (Kongsberg), Mexico (Pachuca, Guanajuato, Zacatecas) and the U.S. (Nevada, Colorado, Montana). On silver, acanthite crystals can appear as black, shiny, acanthus-like leaflets. At temperatures above 173 C, acanthite is converted to Argentite.
Synonyms and Related Terms
acanthus
Other Properties
Luster = metallic Streak = black Cuts like lead; indistinct cleavage
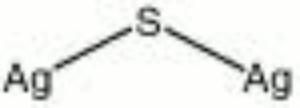
| Composition | Ag2S |
|---|---|
| CAS | 21548-73-2 |
| Mohs Hardness | 2.0 - 2.5 |
| Melting Point | 845 |
| Density | 7.2 - 7.4 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 247.8 |
Hazards and Safety
Sensitive to light.
Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Additional Information
Mineralogy Database: Acanthite
Authority
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: argentite" [Accessed December 11, 2001 (gives conversion temperature as 91 C)
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 Comment: Gives conversion temperature as 173 C