Difference between revisions of "Sawdust"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(username removed) |
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
sciure (Fr.); serrín (Esp.) serrim (Port.); segatura (It.); saw dust; wood dust; fines; powdered wood | sciure (Fr.); serrín (Esp.) serrim (Port.); segatura (It.); saw dust; wood dust; fines; powdered wood | ||
| − | == | + | == Sources Checked for Data in Record == |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 878 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 878 | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 1 May 2016
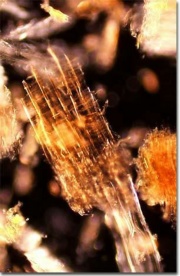
Description
Small particles of wood produced by sawing. Sawdust residues are generated in large amounts at sawmills. It is generally used as a fuel, a soft abrasive or for packing, particle boards, fill materials, paper pulp, and sorbents. Sawdust can also be distilled to produce methanol, resins, and sugars.
Synonyms and Related Terms
sciure (Fr.); serrín (Esp.) serrim (Port.); segatura (It.); saw dust; wood dust; fines; powdered wood
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 878
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sawdust (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)
- Tom Rowland, Noel Riley, A-Z Guide to Cleaning, Conserving and Repairing Antiques, Constable and Co., Ltd., London, 1981
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998