Difference between revisions of "Polypropylene"
RArenstein (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
| − | == Risks == | + | ==Personal Risks== |
| + | Scientific Polymer Products: [http://hazard.com/msds/f2/btq/btqvx.html MSDS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Environmental Risks== | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Collection Risks == | ||
Degraded by ultraviolet light and may contain UV absorbers or antioxidants. Combustible, but slow-burning. | Degraded by ultraviolet light and may contain UV absorbers or antioxidants. Combustible, but slow-burning. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 8 July 2020
Description
A tough, translucent, white, thermoplastic polymer made from propylene. In 1954, Giulio Natta (Milan Polytechnic, Italy) polymerized propylene and, by 1957, polypropylene fibers were being commercially produced by Montecatini Societa Generale (Italy). Polypropylene is similar to Polyethylene, but is slightly less dense with higher gloss, rigidity, and softening point. It has fair abrasion resistance and good resistance to heat and electricity. Polypropylene is used for medical supplies, electrical appliances, toys, bottles, fishnets, pipe, clothing, vapor barrier films, road signs, molded parts, carpet, artificial grass, laminates, food packages, furniture, and photographic enclosures. Polypropylene is also made in a low molecular weight form that is used as greases, sealants, and wax.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PP; polyolefin; polipropileno (Esp.); polypropylène (Fr.); polipropilene (It.); Polypropylen (Deut.); polypropeen (Ned.); polipropileno (Port.); polypropen (Sven.)
Examples: Coroplast; Propylex; Herculon; Microfoam
Applications
Personal Risks
Scientific Polymer Products: MSDS
Environmental Risks
Collection Risks
Degraded by ultraviolet light and may contain UV absorbers or antioxidants. Combustible, but slow-burning.
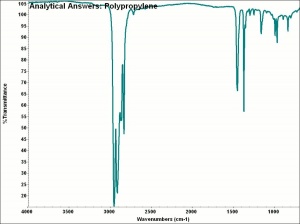
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in some hydrocarbons, isoamyl alcohol. Insoluble in acetone, diethyl ether, lower alcohols, ethyl acetate, acids, alkalis.
Burns with yellow flame and blue center; smells of paraffin.
| Composition | [C3H5]n |
|---|---|
| CAS | 9003-07-0 |
| Melting Point | 160-165 |
| Density | 0.85-0.94 |
Comparisons
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
General Characteristics of Polymers
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 836
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Product Information Comment: Sigma Chemical MSDS has CAS 25085-53-4; Merck has CAS 9003-07-0 as does MSDS for Environmental Science; Scientific Polymer products has 9003-0704 for isotactic polypropylene
- Website address 1 Comment: www.nswpmith.com.au/historyofplastics.html;
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polypropylene (Accessed Nov. 9, 2005)
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000