Difference between revisions of "Apatite"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
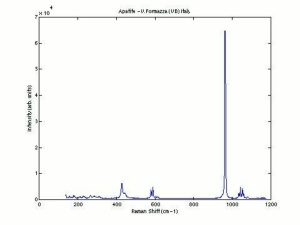
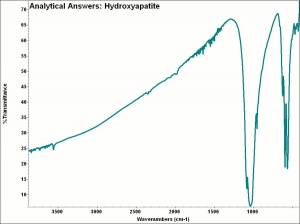
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Apatiteitaly1.jpg~Raman|aaiAPATITE.jpg~FTIR]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Apatiteitaly1.jpg~Raman|aaiAPATITE.jpg~FTIR]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Hexagonal crystals in prismatic and tabular forms; Luster = vitreous to resinous; Streak = white. Transparent to opaque. Fracture = uneven, conchoidal | Hexagonal crystals in prismatic and tabular forms; Luster = vitreous to resinous; Streak = white. Transparent to opaque. Fracture = uneven, conchoidal | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Apatite.shtml Apatite] | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Apatite.shtml Apatite] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 603 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 603 | ||
| Line 47: | Line 45: | ||
* C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | * C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, ''Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals'', Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apatite (Accessed Aug. 30 2005) |
* ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | * ''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia'', Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976 | ||
Revision as of 10:14, 29 August 2020
Description
A naturally occurring mineral of calcium fluor-phosphate. Apatite is found throughout the world with numerous deposits in Europe (Germany, Spain) and North America (Ontario, Massachusetts, California, Mexico). It is colorless when pure, but impurities can give it a white, green (asparagus stone), blue (moroxite), yellow, or violet color. Bones, both human and animal, are composed of hydroxyapatite, mixed with protein (Ossein) and small amounts of other minerals, such as Calcium carbonate. Apatite is commercially used as a fertilizer.
Synonyms and Related Terms
asparagus stone (green); moroxite (blue); fluorapatite; phosphorite; Apatit (Deut.); apatite (Fr., Port.); apatito (Esp.); apatiet (Ned.); apatyt (Pol.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Hexagonal crystals in prismatic and tabular forms; Luster = vitreous to resinous; Streak = white. Transparent to opaque. Fracture = uneven, conchoidal
| Composition | Ca5(PO4)3F |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 4.5 - 5.0 |
| Density | 3.17-3.23 |
| Refractive Index | 1.63-1.67 |
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Apatite
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 603
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Sue Fuller, Rocks and Minerals, DK Publishing, Inc., New York City, 1995
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apatite (Accessed Aug. 30 2005)
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998