Difference between revisions of "Montmorillonite"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
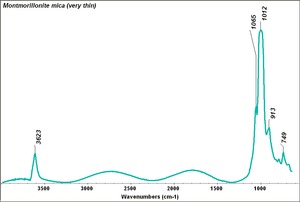
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|Montmorillonite mica (very thin).TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|Montmorillonite mica (very thin).TIF~FTIR (MFA)]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Broad sheets break into irregular fluffy masses. | Broad sheets break into irregular fluffy masses. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
Inhalation can cause lung irritation. | Inhalation can cause lung irritation. | ||
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Montmorillonite.shtml Montmorillonite] | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Montmorillonite.shtml Montmorillonite] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 175 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 175 | ||
| Line 44: | Line 42: | ||
* ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 6341 | * ''The Merck Index'', Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 6341 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Montmorillonite." | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Montmorillonite." Accessed: 15 June 2004.. |
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montmorillonite (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005) |
* Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | * Richard S. Lewis, ''Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993 | ||
Revision as of 09:42, 15 October 2020
Description
A group of Clay minerals that have the ability to absorb large quantities of water. Montmorillonite is a fine-grain, aluminum silicate compound with flat hexagonal crystals. They are formed by the decomposition of basic rocks such as Basalt. Most secondary clays contain some montmorillonite. Some clays high in montmorillonite, such as Bentonite, are highly plastic with high shrinkage rates. Other montmorillonite clays, such as Fuller's earth, are aplastic.
Synonyms and Related Terms
smectite; beidellite; bentonite; fuller's earth; montmorillonita (Esp.); montmorillonite (Fr;); montmorilonite (Port.); Montmorillonit (Deut.); montmorilloniet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Broad sheets break into irregular fluffy masses.
Streak = white
| Composition | Al2O3-4SiO2-H2O |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 1.5-2.0 |
| Density | 2.2-2.7 |
| Refractive Index | 1.480 - 1.630 |
Risks
Inhalation can cause lung irritation.
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Montmorillonite
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 175
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 6341
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "Montmorillonite." Accessed: 15 June 2004..
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montmorillonite (Accessed Sept. 10, 2005)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997