Difference between revisions of "Bentonite"
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
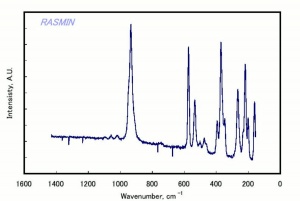
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|benitoniteRS.jpg~Raman]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|benitoniteRS.jpg~Raman]]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == |
Streak = white | Streak = white | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | + | CDH Fine Chemicals: [https://www.cdhfinechemical.com/images/product/msds/41_230021046_BentonitePowder-CASNO-1302-78-9-MSDS.pdf SDS] | |
| − | == | + | == Resources and Citations == |
| − | Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Montmorillonite.shtml Montmorillonite] | + | * Mineralogy Database: [http://www.webmineral.com/data/Montmorillonite.shtml Montmorillonite] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
* R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | * R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, ''Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia'', Dover Publications, New York, 1966 | ||
| Line 56: | Line 54: | ||
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | * ''The American Heritage Dictionary'' or ''Encarta'', via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998 | ||
| − | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: Bentonite. Retrieved May 25, 2003, | + | * ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', http://www.britannica.com Comment: Bentonite. Retrieved May 25, 2003,. |
* ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Francis Turner (ed.), Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York City, 3rd edition, 1942 | * ''The Condensed Chemical Dictionary'', Francis Turner (ed.), Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York City, 3rd edition, 1942 | ||
| − | * Wikipedia | + | * Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bentonite (accessed Sept. 2 2005) |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 96 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 96 | ||
Revision as of 08:45, 15 October 2020
Description
A fine, natural Clay formed from the decomposition of Glass particles in volcanic ash. Bentonite is composed primarily of Montmorillonite. It was named for Fort Benton, Montana, near which it was discovered. Significant deposits have been found in Greece, Japan, Italy, Brazil, Romania, Germany, Mexico, Argentina, Spain, India, Hungary, Poland, Canada, Turkey, Cyprus and the U.S. (California, Montana, Wyoming, Texas, Arizona, Colorado). The light cream to black color aluminum silicate clay retains the texture of the volcanic glass. It occurs primarily in two forms: sodium bentonite or calcium bentonite.
- Sodium bentonites absorb large quantities of water, swelling to about 20 times their original volume to form a jelly-like paste that is smooth like soap. Sodium bentonites are used to increase the plasticity of a ceramic clay body, as emulsifiers in portland cements and concrete, as fillers in insecticides, soaps, paper, and paints; and as a water softener to remove calcium from hard water.
- Calcium bentonites are nonswelling and break down to a finely granular aggregate. They are used as an absorbent clay called Fuller's earth.
Synonyms and Related Terms
montmorillonite; American clay; Wilkinite; colloidal clay; fuller's earth; sodium bentonite; calcium bentonite; soap clay; mineral soap; gumbrin; Bentonite (Deut.); bentonita (Esp.); bentonite (Fr., Port.); bentoniet (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Streak = white
| CAS | 1302-78-9 |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 1.5-2.0 |
| Density | 2.0-2.7 |
Risks
CDH Fine Chemicals: SDS
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Montmorillonite
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Robert Fournier, Illustrated Dictionary of Practical Pottery, Chilton Book Company, Radnor, PA, 1992
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: Entry #102
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: Bentonite. Retrieved May 25, 2003,.
- The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Francis Turner (ed.), Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York City, 3rd edition, 1942
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bentonite (accessed Sept. 2 2005)
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 96
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000