Difference between revisions of "Sodium borohydride"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
White, crystalline powder. Sodium borohydride reacts with many compounds as a reducing agent and an antichlor. It was introduced in the 1970s for use as a weak bleach for wood pulp, textile stains, and foxing spots (concentrations 0.01-1%). Sodium borohydride is used industrially as a scavenger for aldehydes, ketones, acids, esters, chlorides, disulfides, and nitriles in organic solutions. | White, crystalline powder. Sodium borohydride reacts with many compounds as a reducing agent and an antichlor. It was introduced in the 1970s for use as a weak bleach for wood pulp, textile stains, and foxing spots (concentrations 0.01-1%). Sodium borohydride is used industrially as a scavenger for aldehydes, ketones, acids, esters, chlorides, disulfides, and nitriles in organic solutions. | ||
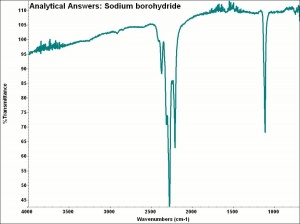
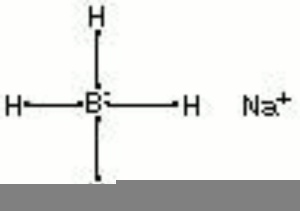
| − | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiNABH4.jpg~FTIR|sodium borohydride.jpg~Chemical structure]]]= Synonyms and Related Terms == | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiNABH4.jpg~FTIR|sodium borohydride.jpg~Chemical structure]]] |
| + | |||
| + | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
sodium tetrahydroborate; sodium hydroboride | sodium tetrahydroborate; sodium hydroboride | ||
Latest revision as of 14:57, 1 June 2022
Description
White, crystalline powder. Sodium borohydride reacts with many compounds as a reducing agent and an antichlor. It was introduced in the 1970s for use as a weak bleach for wood pulp, textile stains, and foxing spots (concentrations 0.01-1%). Sodium borohydride is used industrially as a scavenger for aldehydes, ketones, acids, esters, chlorides, disulfides, and nitriles in organic solutions.
Synonyms and Related Terms
sodium tetrahydroborate; sodium hydroboride
Risks
- Reacts with water to produce hydrogen (highly flammable) and sodium hydroxide.
- Hygroscopic. Slowly decomposes in moist air.
- Flammable. Dangerous fire risk. May be explosive.
- Contact, inhalation, and ingestion results in severe irritation and tissue burns.
- ThermoFisher: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Soluble in water, ethanol, ammonia, amines, pyridine. Insoluble in hydrocarbons, alkyl chloride.
| Composition | NaBH4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 16940-66-2 |
| Melting Point | 36 C |
| Density | 1.07 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 37.83 |
| Boiling Point | 400 C |
Resources and Citations
- S.Adler, "Borohydride: An Alternative to Oxidative Bleaching of Cellulosic Textiles" in Textile Specialty Group Postprints, AIC meeting, 1998.
- I.Block, A.M.Roy, "Treatment of Cellulosic Textiles with Sodium Borohydride" ICOM Preprints, Eighth Triennial Meeting, Sydney Australia, 345-351.
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding a==Resources and Citations==nd the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p.345
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 8735
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986