Difference between revisions of "Toluidine red"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
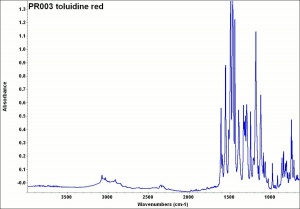
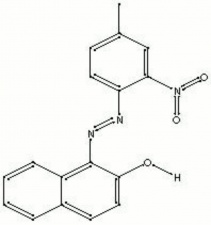
[[[SliderGallery rightalign|PR003 toluidine red.jpg~FTIR|toluidine red.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|PR003 toluidine red.jpg~FTIR|toluidine red.jpg~Chemical structure]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Risks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Ingestion can cause cyanosis. | ||
| + | * Suspected carcinogen. | ||
| + | * Fisher Scientific: [https://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/46042.htm MSDS] | ||
== Physical and Chemical Properties == | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | ||
| − | Soluble in many organic solvents. Insoluble in water | + | * Soluble in many organic solvents. Insoluble in water |
| − | + | * Resistant to acid, alkali and soap. | |
| − | Resistant to acid, alkali and soap. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 31: | ||
| mol. wt. = 307.3 | | mol. wt. = 307.3 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Resources and Citations == | == Resources and Citations == | ||
Latest revision as of 15:03, 10 June 2022
Description
A line of bright, transparent red synthetic azo-type organic pigments. Toluidine reds are based on the reaction of beta-naphthol with 2-nitro-4-toluidine. Toluidine red was first synthesized in 1904 by Lucius and Brüning in Germany. It reached its peak of popular use in the 1970s. In general, toluidine reds have fair lightfastness and weather resistance, but they have a tendency to bleed especially in oil paints. They are used in industrial coatings for air-dried and baked enamels and auto finishes. Toluidine reds are also used in wax crayons, pastels and watercolors.
Synonyms and Related Terms
toluidine toner; rosotoluidine; Pigment Red 3; CI 12120; Hansa red; rouge de toluidine (Fr.);
Risks
- Ingestion can cause cyanosis.
- Suspected carcinogen.
- Fisher Scientific: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soluble in many organic solvents. Insoluble in water
- Resistant to acid, alkali and soap.
| Composition | C17H13N3O3 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 2425-85-6 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 307.3 |
Resources and Citations
- F. Crace-Calvert, Dyeing and Calico Printing, Palmer & Howe, London, 1876
- B. Berrie, S.Q. Lomax, 'Azo Pigments: Their History, Synthesis, Properties and Use in Artists' Materials', Studies in the History of Art , National Gallery of Art, Washington DC, No. 57, 1997
- M. de Keijzer, 'A survey of red and yellow modern synthetic organic artists pigments discovered in the 20th century and used in oil colors', ICOM Preprints Lyons, France, Getty Conservation Institute, Los Angeles, p. 369, 1999
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Reed Kay, The Painter's Guide To Studio Methods and Materials, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1983
- Monona Rossol, The Artist's Complete Health and Safety Guide, Allworth Press, New York, 1994
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000