Difference between revisions of "Polyphenylene sulfide"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A thermoplastic polymer made by the condensation of [[Paradichlorobenzene|p-dichlorobenzene]] and [[sodium|sulfide sodium sulfide]]. Polyphenylene sulfide, or PPS, will not dissolve in any organic solvent at temperatures under 200 C. PPS is often glass reinforced and made into molded parts for connectors, housings, and pump bodies. It is occasionally used as a fiber in protective clothing, although it is stiff and has a low moisture regain. | A thermoplastic polymer made by the condensation of [[Paradichlorobenzene|p-dichlorobenzene]] and [[sodium|sulfide sodium sulfide]]. Polyphenylene sulfide, or PPS, will not dissolve in any organic solvent at temperatures under 200 C. PPS is often glass reinforced and made into molded parts for connectors, housings, and pump bodies. It is occasionally used as a fiber in protective clothing, although it is stiff and has a low moisture regain. | ||
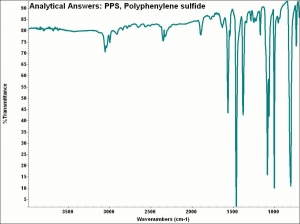
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiPPS.jpg~FTIR]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Examples: Ryton [Amoco Fabrics & Fibers]; Procon [Toyobo]; Toray PPS [Toray] | Examples: Ryton [Amoco Fabrics & Fibers]; Procon [Toyobo]; Toray PPS [Toray] | ||
| − | + | == Physical and Chemical Properties == | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | Resistant to organic solvents and alkalis. Attacked by oxidizing acids and sodium hypochlorite.Moisture regain = 0.6%; Tenacity = ~3 g/denier; Elongation =25-25% | + | * Resistant to organic solvents and alkalis. Attacked by oxidizing acids and sodium hypochlorite. |
| + | * Moisture regain = 0.6%; | ||
| + | * Tenacity = ~3 g/denier; | ||
| + | * Elongation =25-25% | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Melting Point | ! scope="row"| Melting Point | ||
| − | | 185 | + | | 185 C |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row"| Density | ! scope="row"| Density | ||
| − | | 1.38 | + | | 1.38 g/ml |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Resources and Citations== |
| − | * | + | * Textile World at www.textileworld.com/categories/9905/fibers.html |
* Marjory L. Joseph, ''Introductory Textile Science'', Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986 | * Marjory L. Joseph, ''Introductory Textile Science'', Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986 | ||
Latest revision as of 08:55, 18 October 2022
Description
A thermoplastic polymer made by the condensation of p-dichlorobenzene and sulfide sodium sulfide. Polyphenylene sulfide, or PPS, will not dissolve in any organic solvent at temperatures under 200 C. PPS is often glass reinforced and made into molded parts for connectors, housings, and pump bodies. It is occasionally used as a fiber in protective clothing, although it is stiff and has a low moisture regain.
Synonyms and Related Terms
PPS; poly p-phenylene sulfide; polyphenylene sulphide (Br.); poli(sulfuro de fenileno) (Esp.); sulfureto de polifenileno (Port.)
Examples: Ryton [Amoco Fabrics & Fibers]; Procon [Toyobo]; Toray PPS [Toray]
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Resistant to organic solvents and alkalis. Attacked by oxidizing acids and sodium hypochlorite.
- Moisture regain = 0.6%;
- Tenacity = ~3 g/denier;
- Elongation =25-25%
| Melting Point | 185 C |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.38 g/ml |
Resources and Citations
- Textile World at www.textileworld.com/categories/9905/fibers.html
- Marjory L. Joseph, Introductory Textile Science, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Fort Worth, TX, 1986
- Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 79