Difference between revisions of "Nitrile rubber"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "== Authority ==" to "== Sources Checked for Data in Record ==") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A family of synthetic rubbers made by polymerizing acrylonitrile with butadiene. Nitrile rubbers (NBR), first made in the 1940s, are noted for their resistance to oils and solvents. They are used for gloves, gaskets, hoses, shoe soles, kitchen mats, printing rolls, and food-wrapping films. Some NBR is blended with polyvinyl chloride to increase flexibility. With age, nitrile rubbers can oxidize and become brittle. | A family of synthetic rubbers made by polymerizing acrylonitrile with butadiene. Nitrile rubbers (NBR), first made in the 1940s, are noted for their resistance to oils and solvents. They are used for gloves, gaskets, hoses, shoe soles, kitchen mats, printing rolls, and food-wrapping films. Some NBR is blended with polyvinyl chloride to increase flexibility. With age, nitrile rubbers can oxidize and become brittle. | ||
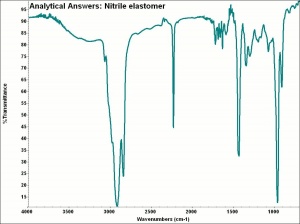
| − | + | [[[SliderGallery rightalign|aaiNITRILE.jpg~FTIR]]] | |
== Synonyms and Related Terms == | == Synonyms and Related Terms == | ||
acrylonitrile butadiene; acrylonitrile rubber; acrylonitributadiene rubber; nitrile-butadiene rubber; NBR; Buna-N; nitrile resin; nitrile elastomer (AAT); acrilonitrilbutadieno (Esp.); goma eloástica de acrilonitrilo (Esp.) | acrylonitrile butadiene; acrylonitrile rubber; acrylonitributadiene rubber; nitrile-butadiene rubber; NBR; Buna-N; nitrile resin; nitrile elastomer (AAT); acrilonitrilbutadieno (Esp.); goma eloástica de acrilonitrilo (Esp.) | ||
| − | == | + | == Risks == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Combustible. | |
| − | + | ==Resources and Citations== | |
| − | + | * M.Baker, E.McManus, "History, Care and Handling of America's Spacesuits" JAIC 31:77-85 1992. | |
* G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 678 | * G.S.Brady, ''Materials Handbook'', McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 678 | ||
| Line 27: | Line 23: | ||
* Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | * Random House, ''Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language'', Grammercy Book, New York, 1997 | ||
| − | + | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000 | |
| − | |||
| − | * Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, | ||
[[Category:Materials database]] | [[Category:Materials database]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 19 October 2022
Description
A family of synthetic rubbers made by polymerizing acrylonitrile with butadiene. Nitrile rubbers (NBR), first made in the 1940s, are noted for their resistance to oils and solvents. They are used for gloves, gaskets, hoses, shoe soles, kitchen mats, printing rolls, and food-wrapping films. Some NBR is blended with polyvinyl chloride to increase flexibility. With age, nitrile rubbers can oxidize and become brittle.
Synonyms and Related Terms
acrylonitrile butadiene; acrylonitrile rubber; acrylonitributadiene rubber; nitrile-butadiene rubber; NBR; Buna-N; nitrile resin; nitrile elastomer (AAT); acrilonitrilbutadieno (Esp.); goma eloástica de acrilonitrilo (Esp.)
Risks
- Combustible.
Resources and Citations
- M.Baker, E.McManus, "History, Care and Handling of America's Spacesuits" JAIC 31:77-85 1992.
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 678
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000