Difference between revisions of "Microballoon"
m (Added image) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
microsphere; microballoons; glass sphere; microesferas de vidro (Port.); Scotchlite [3M] glass bubbles; Zeeosphere [3M]; Microballoon Filler [Top Flite]; 410 Microlight [West Systems] | microsphere; microballoons; glass sphere; microesferas de vidro (Port.); Scotchlite [3M] glass bubbles; Zeeosphere [3M]; Microballoon Filler [Top Flite]; 410 Microlight [West Systems] | ||
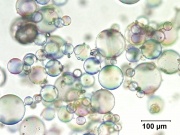
| + | [[File:For CAMEO.jpg|thumb|SEM-BSE image of microballoons in old conservation fill, 410x]] | ||
== Risks == | == Risks == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:55, 18 November 2022
Description
A common name for Glass or Ceramic compounds that are physically formed into microscopic spheres. Microballoons, or microspheres, are finely divided, free-flowing particles that have high strength. The soft, white powder is used as low density extender in plastics and adhesives. Microballoons are also used in industry for filtration systems, as containers for radioactive traces, for thermal insulation layers in nonwoven fabrics, and to form a protective layer over liquid surfaces. In conservation, they have been added to resins to decrease the weight of large filled regions. Examples are:
- Scotchlite glass bubbles [3M]: made from soda-lime/ borosilicate glass;
- Zeeosphere: made from a white opaque ceramic.
Synonyms and Related Terms
microsphere; microballoons; glass sphere; microesferas de vidro (Port.); Scotchlite [3M] glass bubbles; Zeeosphere [3M]; Microballoon Filler [Top Flite]; 410 Microlight [West Systems]
Risks
- Noncombustible. Skin and eye contact can cause irritation.
- 3M Glass Bubbles: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Insoluble in water
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Conservation Support Systems, Catalog, 1997