Saliva
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
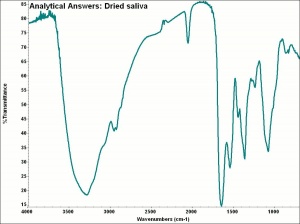
A watery mucus secreted into vertebrate mouths by small glands in the interior of the cheeks, tongue, and palate. Saliva contains water, mucins, proteins, enzymes (amylase, ptyalin), and salts. It serves to moisten the mouth, remove food debris, and breakdown carbohydrates. Saliva has been used as a readily available cleaning agent since ancient times.
Other Properties
Saliva is slightly alkaline.
Soluble in water and dilute alkaline solutions. Insoluble in acetic acid.
Additional Information
P.M.S.Romao, A.M.Alarao, C.A.N.Viana, "Human saliva as a cleaning agent for dirty surfaces" Studies in Conservation Vol 35 (3):153-155, 1990.
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "saliva" Encyclopædia Britannica online, [Accessed April 26, 2002]
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997