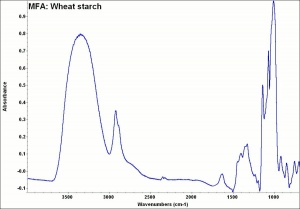
Wheat starch
Description
Polysaccharide granules that compose about 70% of Wheat flour. Wheat starch is separated from the Gluten and fibrous particles by sieving then wash flotation. It is composed of 18-27% Amylose. When heated with Water, wheat starch forms a low viscosity solution that does not change with heating time. It thickens substantially on cooling and to form an opaque gel. Wheat starch dries to form a strong bond. It is susceptible to biological attack and may turn gray or yellow with age. Wheat starch is the primary adhesive used by paper conservators for hinging, mending, lining ,and reinforcement (AIC Book and Paper Catalog).
Synonyms and Related Terms
almidón de trigo (Esp.); amidon de blé (Fr.); amido di grano (It)
Examples include: Aytex P [Henkel]; Starbake starch [Hercules]; Paygel [General Mills]; Sin-nori; Jin-Shofu
Other Properties
Fine oval shaped granules. Granule size = 3 - 35 micrometers
Gelatinization temperature = 58 - 64 C
Turns blue-violet with iodine.
Hazards and Safety
Susceptible to biodeterioration. Dried films become brittle with age.
Talas: MSDS
Additional Images
Authority
- Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Jane Down, Adhesive projects at the Canadian Conservation Institute, Preprints of the SSCR's 2nd Resins Conference, Sept. 1995, Scottish Society for Conservation & Restoration, Edinburgh
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 768
- Conservation Support Systems, Catalog, 1997
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000