White oak
Description
A large oak, Quercus alba, native to eastern North America. White oak has a light brown, coarse-grain wood that is strong. The high quality wood is used for lumber, millwork, and flooring.
Synonyms and Related Terms
Quercus alba; chêne blanc (Fr.); carvalho branco americano (Port.); stave oak; roble; roblecito; mamecillo; encino; cucharillo
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Medium tree growing to 30 m with spreading, oval crown
- Bark=light brown with blocky patches or scales
- Leaves=oblong (10-16 cm) with 7 to 10 rounded lobes.
- Fruit=long, oval acorn with warty cap, maturation takes one year
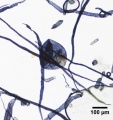
Paper fiber type: hardwood, ring porous. Using transmitted light microscopy, pulp is identified by two sizes of vessels with profuse pitting. The smaller late wood vessels of white oak will stain similarly to the early wood vessels, which can help distinguish pulp from Red oak. Vasocentric trachieds are worm-like and heavily pitted. Perforations are simple. Tyloses may be present. Appearance with Graff "C" stain: dark blue, but varies with bleaching. Average dimensions of fibers: length 1.47, 14-22μm wide. Common pulping method: kraft.
Additional Images
Resources and Citations
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 555
- Dictionary of Building Preservation, Ward Bucher, ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York City, 1996
- Virginia Tech Dendrology website at www.fw.vt.edu/dendro/dendrology/main.htm (accessed Oct. 8, 2005)
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_oak (Accessed Oct. 8, 2005)
- Marja-Sisko Ilvessalo-Pfäffli. Fiber Atlas: Identification of Papermaking Fibers (Springer Series in Wood Science). Springer, 1995.
- Walter Rantanen. "Fiber ID Course." Integrated Paper Services. June 2013. Lecture.