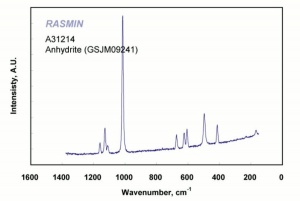
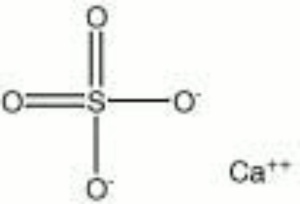
Calcium sulfate, anhydrous
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
White, odorless crystals whose mineral form is called Anhydrite. Anhydrous calcium sulfate is ground to form a colorless, inert pigment which is often used as a paper filler. It is strongly hygroscopic and is also used as a drying agent for solids, organic liquids, and gases. Anhydrous calcium sulfate is commercially sold under the name of Drierite®. Its drying capacity can be regenerated an unlimited number of times.
Synonyms and Related Terms
anhydrite; karstenite; muriacite; anhydrous sulfate of lime; anhydrous gypsum; Drierite
Risks
- IntegraChem: SDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Slightly soluble in water.
| Composition | CaSO4 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 7778-18-9 |
| Mohs Hardness | 3.0 - 3.5 |
| Melting Point | 1450 C |
| Density | 2.93-2.964 g/ml |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 136.14 |
| Refractive Index | 1.570; 1.614; 1.575 |
Resources and Citations
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: 'anhydrite' [Accessed December 4, 2001]
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density=2.93 ref. index=1.570; 1.614; 1.575
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979