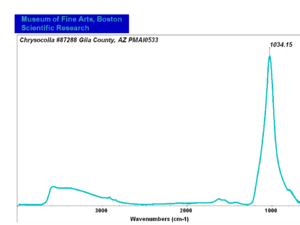
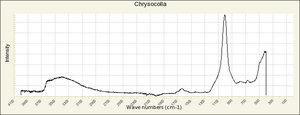
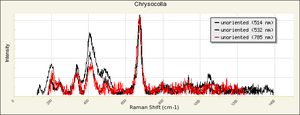
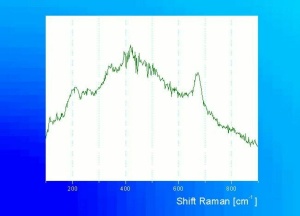
Chrysocolla
Description
A sky blue mineral composed of hydrated copper silicate. Chrysocolla is a secondary copper ore that has also been used as a Gemstone and a blue-green pigment. It has been gathered or mined as a semiprecious stone since 3000 BCE. Chrysocolla is mined in England (Cornwall, Cumberland), Congo, Zaire, Chile, and the U.S. (Pennsylvania, Arizona, New Mexico and Utah). The translucent to opaque stone is sky-blue in its natural state, but appears green when ground into a fine powder; it can be unevenly colored and resemble turquoise. Chrysocolla has been found as a pigment in wall painting at Kizil in Turkistan and in Twelfth Dynasty Egyptian tombs (Gettens and Stout 1966). In the 16th and 17th centuries, it was used as a watercolor pigment called cedar green. Chrysocolla is stable to light but is decomposed by acids, alkalis, and heat.
Synonyms and Related Terms
cedar green; copper silicate; gold solder; chryzokola (Pol.); crisocola (Port.); Chrysokoll (Deut.); chrysocolle (Fr.); chryssokolla (Gr.); crisocolla (It.); crisocola (Esp., Port.); chrysocolla (Ned.)
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Orthorhombic crystal system with massive, nodular or botryoidal crystals
- Cleavage = none
- Fracture = uneven to conchoidal
- Luster = vitreous to dull
- Streak = white or pale blue-green
- Fluorescence = generally inert
- Pleochroism = from pale green to colorless
- Pigment particles are anisotropic with high birefringence, and straight extinction
| Composition | CuSiO3-nH2O |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 2.5 - 3.5 |
| Density | 2.0-2.8 g/ml |
| Refractive Index | 1.575; 1.598; 1.597 |
| Birefringence | 0.023-0.050 |
Comparisons
Characteristics of Common Blue Pigments
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Chrysocolla
- Gem Identification Lab Manual, Gemological Institute of America, 2016.
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966 Comment: density =2.4, ref. index=1.575; 1.598; 1.59
- R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Jack Odgen, Jewellery of the Ancient World, Rizzoli International Publications Inc., New York City, 1982
- Kurt Wehlte, The Materials and Techniques of Painting, Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1975 Comment: p. 52
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Thomas B. Brill, Light Its Interaction with Art and Antiquities, Plenum Press, New York City, 1980 Comment: ref.index.1.575; 1.598; 1.597
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: Chrysocolla. Retrieved May 25, 2003. (tech info-ref. index = 1.45; 1.55)
- Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chrysocolla Chrysocolla) (Accessed Sept. 2, 2005 and Dec 2022) hardness=2.5-3.5
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 232
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, https://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000