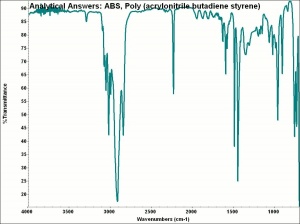
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
Description
A family of thermoplastic polymers prepared by either grafting styrene and acrylonitrile onto an elastomeric polybutadiene backbone or by mechanically blending rubber copolymer matrices of styrene-acrylonitrile with butadiene-acrylonitrile. Varying the ratios of the three monomers produces a wide range of properties. Acrylonitrile provides resistance to chemicals, high temperatures, and creep deformation while butadiene adds toughness and styrene gives high modulus of elasticity and low cost. The standard grade of ABS resin is strong, resilient, and difficult to break. The polymer can be injection molded or extruded into numerous shapes. ABS resin is used for appliances, automobile parts and fittings, telephones, radios, televisions, pipes and conduits, luggage, boats, toys, and bottles.
Synonyms and Related Terms
ABS; acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin; resina de acrilonitrilo-butadieno-estireno (Esp.); resina de acrilonitrilo-butadieno-estireno (Port.)
Examples: Abson; Cycolac
Other Properties
Resistant to water, salts and oils. May be degraded by oxidizing acids and many organic solvents (aromatics, ketones, and alcohols).
Hazards and Safety
Combustible, slow-burning, generates smoke.
Comparisons
General Characteristics of Polymers
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
Authority
- G.S.Brady, G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 12
- Pam Hatchfield, Pam Hatchfield, Pollutants in the Museum Environment, Archetype Press, London, 2002
- Sharon Blank, Sharon Blank, An introduction to plastics and rubbers in collections, Studies in Conservation, 35, 53-63, 1990
- Theodore J. Reinhart, Theodore J. Reinhart, 'Glossary of Terms', Engineered Plastics, ASM International, 1988