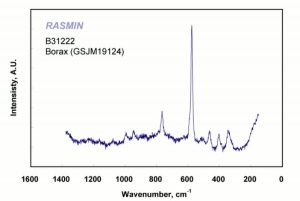
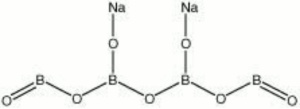
Borax
Description
A natural product composed of hydrated borate sodium borate. Borax is produced by the evaporation of water in shallow lakes. Borax was used by the Egyptians for mummification and by the Romans for glassmaking. In the 9th century, it was used as a flux for soldering gold in Arabia and by the 10th century, borax was being used in ceramic glazes in northern China. By the 13th century, tincal (borax) was regularly imported from Tibet to Europe for use in Venetian glass. The white powder is now mined from deposits in India, Russia, Persia, and the U.S. (California). Borax is used as a flux, cleansing agent, tanning agent, water softener, preservative, fungicide, and as an alkaline ingredient in glass, ceramics, and glazes.
Synonyms and Related Terms
sodium borate decahydrate; sodium diborate; tincal; tincalconite; tincar; hydrated sodium boration; sodium tetraborate; rasorite; Sporax; brax (Esp., Port.); borace (It.)
Other Properties
Soluble in water. Sweetish, alkaline taste.
Cleavage is perfect in one direction, good in another.
Translucent to opaque.
Fracture = conchoidal. Streak = white. Luster = vitreous to greasy.
| Composition | Na2B4O7.10H2O |
|---|---|
| CAS | 1303-96-4 |
| Mohs Hardness | 2.0 - 2.5 |
| Melting Point | 75 |
| Density | 1.715 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 381.4 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4630 (fused) |
| Boiling Point | 320 |
Hazards and Safety
Toxic by ingestion. LD50 = 4500-6000 mg/kg. Skin contact can cause irritation.
LINK: International Chemical Safety Card
Additional Information
Mineralogy Database: Borax
Authority
- G.S.Brady, G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 108
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Borax (Accessed Sept. 2, 2005)
- Hermann Kuhn, Hermann Kuhn, Conservation and Restoration of Works of Art and Antiquities, Butterworths, London, 1986
- S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, S.R.Trotman, E.R. Trotman, Textile Analysis, J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1932
- Michael McCann, Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- George Savage, George Savage, Art and Antique Restorer's Handbook, Rockliff Publishing Corp, London, 1954
- G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, G.Caneva, M.P.Nugari, O.Salvadori, Biology in the Conservation of Works of Art, ICCROM, Rome, 1991
- Richard S. Lewis, Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Susan E. Schur, Susan E. Schur, Conservation Terminology: A review of Past & Current Nomenclature of Materials, Technology and Conservation, Spring (p.34-39); Summer (p.35-38); Fall (p.25-36), 1985
- Book and Paper Group, Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: ref. index=1.4630
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: borax" Encyclopdia Britannica [Accessed December 4, 2001