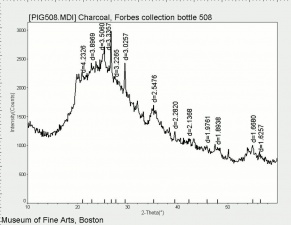
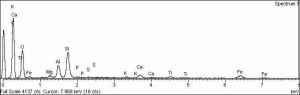
Charcoal
Description
A black, porous carbonaceous material. Charcoal is the carbon containing residue from burned wood (e.g., willow, maple, beech, linden or (tree) plum) or other organic containing materials such as bone, plants or animals. Charcoal contains 80 to 98% carbon with some ash and moisture. Charcoal has been used since ancient times as a drawing material and pigment (see black charcoal black). Charcoal is also sold commercially as a fuel, abrasive, sorbent, filter media, and decolorizer.
See also carbon activated carbon, and crayon charcoal crayon.
Synonyms and Related Terms
trkul (Dan.); negro carbn (Esp.); carbn vegetal (Esp.); Holzkohle (Deut.); charbon de bois (Fr.); karboyno (Gr.); carbonella (It.); carbone (It.); carbo ligni (Lat.); houtskool zwart (Ned.); carvo vegetal (Port.)
Other Properties
Microscopically, tiny wood splinters may be visible.
| Density | oak=0.57; pine=0.28-0.44 |
|---|
Hazards and Safety
Fire risk. May ignite spontaneously in air.
Additional Images
Authority
- G.S.Brady, G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 182
- Ralph Mayer, Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- R.D. Harley, R.D. Harley, Artists' Pigments c. 1600-1835, Butterworth Scientific, London, 1982
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charcoal (Accessed Sept. 2 2005)
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density for oak=0.57; pine=0.28-0.44
- Richard S. Lewis, Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Random House, Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998