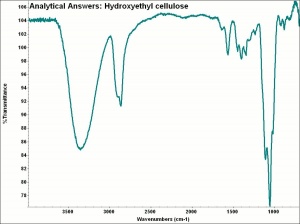
Hydroxyethyl cellulose
Description
A cellulose ether with a hydroxyethyl functional group substitution. Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) is a nonionic thermoplastic polymer that is soluble in water as well as many organic solvents. It is a white granular solid that is used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, agent thickener, and film former in many types of solutions such as foods, cosmetics, paints, and glazes. It is also used as a sizing agent and consolidant. Hydroxyethyl cellulose discolors and becomes insoluble with thermal aging (Feller and Wilt 1990).
Synonyms and Related Terms
HEC; hydroxyethylcellulose; hidroxietilcelulosa (Esp.); hidroxietilcelulose (Port.)
Examples: Natrosol [Aqualon]; Cellosize [Dow]; Tylose H [SE Tylose]
Other Properties
Soluble in water, ethylene glycol. Insoluble in ethyl ether. pH = 6.5-8.5. Softening point = 135-140C.
| Refractive Index | 1.51 |
|---|
Additional Information
R.Feller, M.Wilt, Evaluation of Cellulose Ethers for Conservation, in Research in Conservation Series, Getty Conservation Institute, 1990.
Comparisons
Physical Properties for Selected Thermoplastic Resins
General Characteristics of Polymers
Authority
- Book and Paper Group, Book and Paper Group, Paper Conservation Catalog, AIC, 1984, 1989