Talc
Description
A soft, slippery mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate. Talc is found in veins and masses in metamorphic rocks; large deposits occur in Austria (Tyrol), Italy (Florence), Switzerland, Germany (Bavaria), England (Cornwall), Scotland (Shetland), Canada (Quebec, Ontario), and the U.S. (New England, New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, North Carolina, Texas). Talc, mixed with other minor minerals, occurs in the stone called Steatite, or soapstone. It is usually a white, green or gray color. Talc is so soft, it can be scratched with a fingernail. It has a waxy luster and a greasy feel. Steatite was used in antiquity for small carved objects, such as cylinder seals, scarabs, amulets, bowls, boxes, beads, and statuary. After carving, some pieces were baked to dehydrate the talc and thus harden the stone. Currently, talc is often crushed and used as a filler in paper, ceramics, paint, plastics, rubber, soaps, plaster, crayons, and cosmetics. It has also been used as a lubricant, leather dressing, dusting powder, and as an insulating material. Talc is used on the inside of powdered gloves and can leave residual powder on contacted surfaces. Since soapstones are resistant to most chemical reagents, and to moderate heat, they have been used for sinks and countertops.
Synonyms and Related Terms
hydrated magnesium silicate; Pigment White 26; talc (Fr.); talk (Ned., Sven., Pol.); talco (Esp., It., Port.); Talk (Deut.); Talkum (Deut.); talkis (Gr.); talcum; soapstone; steatite; asbestine; French chalk; tailors chalk; Mistron®; Vertal; Nicron®;
Risks
Noncombustible. Some samples may contain asbestos.
Talc USA: MSDS
Physical and Chemical Properties
Ground particles can be very small (2.0 micrometers).
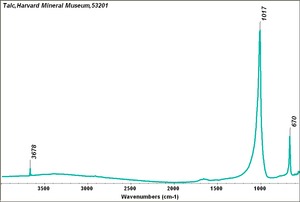
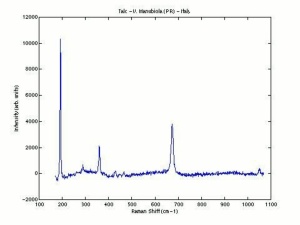
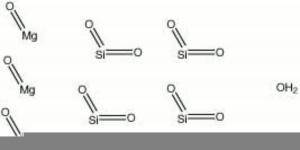
Talc occurs naturally in foliated masses. Perfect cleavage in one direction producing thin laminar particles. Streak = white. Fracture = uneven. Luster = pearly, greasy.
Strongly birefringent under crossed polars
Insoluble in water, cold acids or alkalis
| Composition | Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 |
|---|---|
| CAS | 14807-96-6 |
| Mohs Hardness | 1.0 |
| Density | 2.5-2.8 |
| Molecular Weight | mol. wt. = 379.3 |
| Refractive Index | 1.539; 1.589; 1.589 |
Comparisons
Properties of Common Abrasives
Characteristics of Common White Pigments
Resources and Citations
- Mineralogy Database: Talc
- Nicholas Eastaugh, Valentine Walsh, Tracey Chaplin, Ruth Siddall, Pigment Compendium, Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- G.S.Brady, Materials Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971 Comment: p. 793
- Encyclopedia Britannica, http://www.britannica.com Comment: "talc" [Accessed March 4, 2002].
- C.W.Chesterman, K.E.Lowe, Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Rocks and Minerals, Alfred A. Knopf, New York, 1979
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talc (Accessed Sept. 17, 2005)
- The Dictionary of Paper, American Paper Institute, New York, Fourth Edition, 1980
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Richard S. Lewis, Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 10th ed., 1993
- Michael McCann, Artist Beware, Watson-Guptill Publications, New York City, 1979
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia, Douglas M. Considine (ed.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1976
- Random House, Webster's Encyclopedic Unabridged Dictionary of the English Language, Grammercy Book, New York, 1997
- The Merck Index, Martha Windholz (ed.), Merck Research Labs, Rahway NJ, 10th edition, 1983 Comment: entry 9207
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Robert Weast (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, v. 61, 1980 Comment: density=2.7-2.8