Refracted light
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Description
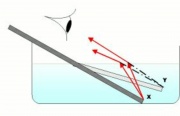
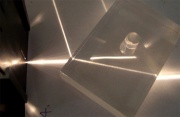
The change in angle of a light path as it passes from one medium into another with a different refractive index. The amount of deflection is proportional to the ration of the refractive indices of the two media. Refraction causes a straight object, like a pencil, appear to bend and the interface of two mediums, such as Air (refractive index = 1.00) and Water (refractive index=1.33). Refraction is responsible for rainbows and for dispersing white light into the spearate colors as it passes through a Prism.
Synonyms and Related Terms
"refraction; refraktion (Dan.); gebrochenes Licht (Deut.); refracción (Esp.); lumière réfractée (Fr.); rifrazione (It.); lichtbreking (Ned.); refração (Port.) "
Sources Checked for Data in Record
- R. J. Gettens, G.L. Stout, Painting Materials, A Short Encyclopaedia, Dover Publications, New York, 1966
- Ralph Mayer, A Dictionary of Art Terms and Techniques, Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 1969 (also 1945 printing)
- Walter C. McCrone, John Gustave Delly, The Particle Atlas, W. McCrone Associates, Chicago, IV, 1972
- Matt Roberts, Don Etherington, Bookbinding and the Conservation of Books: a Dictionary of Descriptive Terminology, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1982
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, at http://www.wikipedia.com Comment: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Refraction (Accessed Sept. 20, 2005)
- The American Heritage Dictionary or Encarta, via Microsoft Bookshelf 98, Microsoft Corp., 1998
- Art and Architecture Thesaurus Online, http://www.getty.edu/research/tools/vocabulary/aat/, J. Paul Getty Trust, Los Angeles, 2000