Fiber optics reflectance spectroscopy (FORS)
Description
One technique used to measure the spectral curve li light reflected from a colored surface. Fiber Optic Reflectance spectroscopy (FORS) is a non-invasive analysis technique that can identify some types of colorants. It uses a fiber optic probe and a pulsed xenon source to provide good sensitivity to examine small areas with a specific wavelength of light then measure the spectral reflectance emitted from the impinged area. The fiber optics probe minimizes the interference from ambient light. The identification of a pigment based on its reflectance is based on the comparison of standards that were prepared as closely as possible to the artist techniques.
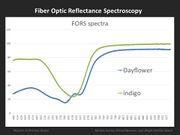
For the Japanese woodblock prints of the Edo period (see Ukiyo-e Colorants), the most common blue colorants were dayflower, indigo, and later Prussian blue are easily identified by FORS as shown in the graph. This identification can be accomplished, not only in blue printed areas, but also in greens and purples, which are a combination of a blue and another colorant (yellow, red).
Synonyms
Color spectroscopy
Resources and Citations
- IFAC: FORS reference spectra database
- CHSOS: Pigment Checker Database
- National Gallery of Art, Scientific Research: Glossary of Conservation Terminology